* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution_3
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
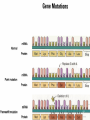
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
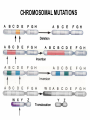
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
What is Evolution? 1 Evolution • Definition: to unroll, unfold, or change. • Anything can change • Word “evolution” brings to mind thoughts of an amoeba changing over millions of years into a human. • We need to clarify what kind of “change” we are discussing. 2 Changes: Big and Small The word “evolution” is used in different ways - one true, the other not. Both evolutionists and creationists believe in changes that have come upon the world. “Micro-evolution” - the adaptation of populations through natural selection is well-proven (Changes within a kind) 3 Changes: Big and Small Special Theory of Evolution or “Microevolution” which describes small changes that do not cross “phylogenetic boundaries.” This is change within groups (i.e. dogs, german shepherds, pit bulls and poodles) but doesn’t allow changes from one group to another (i.e. fish to amphibian to reptile, etc.) 4 Changes: Big and Small • “Macro-evolution” - change beyond the species level (One kind becomes another kind) 5 Changes: Big and Small • General Theory of Evolution or “Macroevolution” is the theory that all the living forms in the world have arisen from a single source which itself came from an inorganic form. • Problem with “macroevolution” is that it goes against what we have observed in nature, in that it does not recognize the limits of change. 6 Small changes do occur, but eventually those changes come to a genetic barrier that is impossible to cross. Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus species KIND? 7 BIBLE “KINDS” • Comes from Hebrew word “min” Occurs 31 times in Old Testament • Not equivalent to word species • New species can be formed but new kinds cannot • “Cattle” in Gen. 1:25 & “Hawk” in Lev. 11:16 8 Charles Darwin’s Theory • “Father of evolutionary theory” • Originally believed in God but later believed in power of nature • Church of England taught the “fixity of species” • In study of nature found that organisms do change • Did not understand that the Bible and the facts of nature agree. 9 Finches of the Galapagos Islands • 1835 • Studied finches • Thought if nature could change size and shape of beaks in a few years—what could nature change in a few million years? 10 Finches of the Galapagos Islands • Study has continued for past 160+ years—finches have always had beaks. • The only thing that “Darwin’s finches” prove is that a finch always stays a finch. 11 Natural Selection • “Survival of the fittest” –center of evolutionary thought. • Creationists have never objected to the idea of natural selection. Could it be the Creator’s plan for preventing harmful mutations from destroying an entire species? • Cannot cause one kind of organism to “evolve” into another kind of organism. 12 Genetic Mutations • Now coupled with Natural Selection to explain evolution. • Changes in the DNA structure which are passed from parent to offspring. • We are told that “nature” has “selected” certain beneficial mutations and plugged them into various organisms, eventually causing those organisms to change from one kind to 13 another. DNA STRUCTURE 14 DNA TO PROTEIN SEQUENCE 15 CHROMOSOMAL MUTATIONS 16 17 Genetic Mutations • Mutations are random • Mutations are very rare. “It is probably fair to estimate the frequency of a majority of mutations in higher organisms between one in ten thousand and one in a million per gene per generation.” • Good mutations are very, very rare. Three kinds: good, bad and neutral. Over 99% are harmful in some way. 18 Genetic Mutations Color blindness is a common genetic mutation 6 % of males; ½ % of females. 19 Genetic Mutations George Gaylord Simpson (famous evolutionist from Harvard University) admitted that if there were a population of 100 million individuals, and they produced a new generation every day, the likelihood of obtaining good evolutionary results from mutations could be expected once every 274 billion years! “Unless there is an unknown factor tremendously increasing the chance of simultaneous mutations, such a process has played no part whatever in evolution.” 20 Genetic Mutations • Remember, mutations do not create genetic information, they only alter existing information. • Natural selection plus mutations still does not answer the question of life’s origin of living things. 21 OTHER “PROOFS” OF EVOLUTION 22 ERNST HAECKEL’S HOAX • Ontogeny Recapitulates Phylogeny • Human baby goes through different evolutionary stages as it grows • Human embryos never have gill slits like fish • Humans do not go through a “rabbit-like” or “lizard-like” stage. • Humans are humans 23 English Peppered Moth 24 English Peppered Moth • No new genetic material was created to form the black moth. • Moths were still moths. • Change can occur but there are limits. 25 Did Horses Evolve? 26 Did Horses Evolve? • The horse series was constructed from fossils that do not fit together. • The animals have different numbers of ribs and vertebrae. • George Gaylord Simpson (famous evolutionist) said “The uniform, continuous transformation of Hyracotherium into Equus, so dear to the hearts of generations of textbook writers, never happened in nature.” 27 Did Horses Evolve? The proof for horse (camel, whale) evolution is mainly bound up in the work of an artist with a good imagination. 28 Are Things that Look Similar Always Related? • Homologous structures • Evolutionists conclude that all these animals must be related. • Creationist says this is evidence of a common designer. 29 Are there “Leftovers” of Evolution? • Vestigial Organs • Over 100 parts of the human body (tonsils, appendix, wisdom teeth, coccyx, etc.) • Appendix is lymphoid tissue which helps produce white blood cells to fight disease. 30 Vestigial Organs • Tonsils help fight off germs • Wisdom teeth help in grinding of food (if jaw is large enough) • Coccyx serves as a point of attachment for pelvic muscles that help us stand up. Also in sitting more comfortably. • Creationists recognize the word “vestigial” as meaning “intended purpose not yet known.” 31 Powerful Point If man does have over 100 vestigial organs, then in the past he would have had more organs than he now has. In the past, he would have been developing the organs that he presently has, plus he would have had the 100+ functional vestigial organs. So the farther back we go in time, the more complex the organism becomes. Yet, evolutionary theory states that organisms become more complex over time. How can both of these teachings be correct? Evolution is the rise of new, different, and functioning organs, not the wasting away of alreadypresent complex organs. 32 God designed the body perfectly. There are no leftovers of evolution. 33