* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Climate Change Impacts in the Context of Economic
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Saskatchewan wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
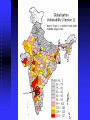
Double Exposure: Climate Change Impacts in the Context of Economic Globalization Concepts Double Exposure: Regions, sectors, ecosystems, and social groups will be confronted by both the impacts of climate change and consequences of globalization. New patterns of winners and losers will emerge. What does exposure to multiple stressors mean for vulnerability? Vulnerability is dynamic. In the case of agriculture, structural economic changes must be addressed at the same time as environmental changes. Case Studies Southern Africa India Cuba Double Exposure: Assessing Vulnerability to Climate Change and Economic Globalization in India Assessing vulnerability CICERO, Rutgers, TERI, IISD study supported by CIDA and Norwegian Foreign Ministry Methodology: Macro-level vulnerability profile, local case studies, policy analysis Goal: Identify highly vulnerable districts to identify the factors that enhance or constrain coping and adaptive capacity Elements of vulnerability profiles Biophysical vulnerability • Soil degradation and cover • Flood prone districts • Groundwater extraction Base vulnerability index Socioeconomic vulnerability • Agricultural workers and laborers • Irrigation availability • Literacy • Infrastructure • Gender discrimination Climate sensitivity index (precipitation variability and dryness) Trade sensitivity index (port distance and export- & importcrops) Climate change vulnerability Globalization vulnerability Case Studies How are farmers influenced by economic changes? How do they cope with climate variability? How may global changes influence adaptive capacity? ANANTAPUR ANANTAPUR Anantapur District, Andhra Pradesh Small and marginal farmers, landless laborers Dry, rainfed agriculture Most land devoted to groundnut production Profitability reduced in 1990s due to growing cost of cultivation, stagnation or decrease in output prices, consecutive drought, and pest problems Desperate situation has led to suicides among farmers Groundnut production Sufficiency in edible oils gained by early 90s (97% in ’92/93). Opening of the Indian edible oil market to imports Palm oil from Indonesia and Malaysia has been a main competitor Domestic edible oil prices move with international prices; good crop plus oversupply of imports means low prices. Duty hikes in India (to protect farmers) often ineffective because of excess production and drops in international prices Implications for farmers Profitability is being squeezed Difficult to repay creditors ”Oilseed industry is dying” Lack of an alternative rainfed crop that is viable for small and marginal farmers Options: Leave agriculture Double Exposure Climate variability and change is an added stress to farmers; in some case, it is what pushes them over the edge. Vulnerability to global environmental change must be assessed within the context of multiple stressors.