* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MCB 135E Discussion October 11-15
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
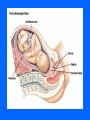
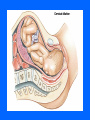
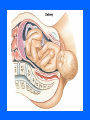
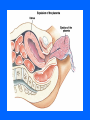
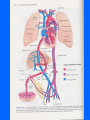
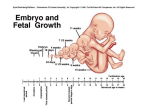
MCB 135E Discussion October 11-15 Mid-Term I • Average 87 (+/- 9) • Key available in hallway near 102 Donner Topics • Labor and Delivery • Cardio-respiratory Changes After Birth • The Normal Newborn Labor and Delivery • Parturition • Hormones • Delivery Phase Parturition • Birth Process – 38 Weeks after fertilization – 40 Weeks after last menstrual period • Onset of Labor – Process that is not completely understood, but involves a combination of mechanical and hormonal factors Hormones • • • • • • Fetal Hormones Estrogen Progesterone Oxytocin Prostoglandins Relaxin Delivery Phases • Dilation and Effacement • Descent and Expulsion • Expulsion of the Placenta Cardio-Respiratory Changes • • • • • Heart Development Cardiac Outflow Anomalies Normal Fetal Circulation Fetal Cardiac Function Transitional Physiology Fetal Cardiac Function • In adult: – Hypothalamic control of cardiac output • Increase Heart Rate • Increase Contractile force of myocardium • In fetus – Contractile force is at a maximum – Control cardiac output only through increased heart rate Transitional Physiology • Changes in fetal circulation at birth: – Loss of placenta – Opening of pulmonary arteries – Functionality of the lungs • Blood is allowed to flow to lungs due to less pressure (the path of least resistance) – Apoptosis of fetal modifications The Normal Newborn • Respiration • Assessment of Transition • What to Expect Respiration • First breath – Responsible for opening of lungs – 30-100mmHg in newborn vs. 5-10 mmHg normal • Close ductus arteriosus – First functional, later anatomical • Removal of lung fluid Transition • Apgar Scoring • The first hours of life • Primary vs Secondary Apnea What to Expect… • The first week of life: – Vitamin K • control blood clotting and is essential for synthesizing the liver protein that controls the clotting (thrombin) – Antibiotic Eye Drops – Hepatitis B Vaccine – Feeding • Increase intake until 1 fluid ounce per hour of milk is consumed – Jaundice • Indicator of postbirth adaptations • Caused by an incomplete metabolism of bilirubin – Bilirubin is a waste product of hemoglobin breakdown