* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Growth and Development of the Respiratory, Cardiovascular
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
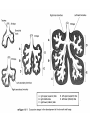
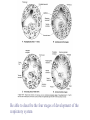
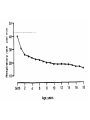
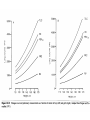
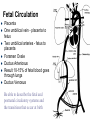
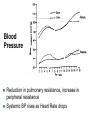
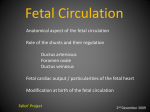
Growth & Development of the Respiratory & Cardiovascular Systems Be able to describe the four stages of development of the respiratory system Lung Growth Alveolar development – last trimester, most postnatally, – 20 million at birth, – 300 million at 8 (adult) Fetal respiratory movements Lung weight: – 60-70gm at birth – increasing 20 fold to adulthood, – correlates best with height Spirometry Be able to describe the development of the heart Endocardial tubes form, that eventually coalesce to form the primitive heart tube at 3 weeks Heart beats soon after Nearby angiogenic cells (mesodermal) form in clusters (blood pools) and migrate to form endothelial lining of blood vessels Adjacent mesenchymal cells migrate around endothelial lining to form vessel wall 6th week - heart has developed its general definitive form 8th week - blood vessels are formed Heart tube folds and twists forming four distinct chambers Fetal Circulation Placenta One umbilical vein - placenta to fetus Two umbilical arteries - fetus to placenta Foramen Ovale Ductus Arteriosus Result 10-15% of fetal blood goes through lungs Ductus Venosus Be able to describe the fetal and postnatal circulatory systems and the transitions that occur at birth Fetal Circulation Umbilical vein - Oxygen saturation = 70% Fetal Periphery - Oxygen saturation = 55% After birth – Arterial = 97% – Venous = 70% fetal hemoglobin -greater affinity for Oxygen Birth Adjustments Lungs expand, pulmonary vascular resistance decreases and systemic blood pressure rises Left atrial pressure rises - foramen ovale closes Ductus Arteriosus flows in opposite direction until vasoconstriction and eventual closure Heart Size Left side grows faster after birth Heart growth curve same as weight (fat free mass) 40 ml at birth, 600 - 800 ml as adult – doubles by 6 months, – quadruples by 2 years, Heart Rate, Stroke Volume Heart rate: 140 bts/min (sd = 20) at birth Stroke Volume: – 3-4 ml at birth, 40 ml just before growth spurt, 60 ml as adult Cardiac Output: – 0.5 l/min at birth, 5 l/min as adult Blood Pressure Reduction in pulmonary resistance, increase in peripheral resistance Systemic BP rises as Heart Rate drops Blood Composition BloodVolume: Highly correlated with heart size and body weight, and maximum oxygen uptake Hematocrit: – Adult 30% at 2 months of age, – sex difference established at puberty Red blood cell count and hemoglobin concentration similar pattern – males 40-45%, females 38-42% Thermoregulation HEAT BALANCE & TEMPERATURE REGULATION METABOLISM: CHEMICAL REACTIONS: HEAT & ENERGY HEAT LOSS: – – – – RADIATION, CONDUCTION, CONV ECT ION EVAPORATION (skin & lungs) WARMING INSPIRED Al R URINE & FAECES CONTROL: – – – H Y P OT H A LAM U S PERIPHERAL RECEPTORS Comparison of core and peripheral temperatures 70% 27% 2% 1% CONTROL IN NEWBORNS Mechanisms of shivering & sweating are poorly developed Sweat glands immature Large S.A./ Wt ratio Thin subcutaneous adipose tissue layer LEADS TO INSTABILITY OF BODY TEMPERATURE Average body temperature drops with age SD also drops, indicating better control CONTROL IN NEWBORNS Vasoconstriction well developed Crying increases metabolic rate Restlessness & increased movements Brown fat Vulnerability of the Adolescent Athlete There have been several deaths of adolescent athletes – – – – – Intense prolonged activity High ambient temperature & humidity Athletic equipment Big (small S.A. /Weight ratio) Lack of water HEAT STROKE Sweating (Sweat is hypotonic) Water leaves cells to hypertonic exterior Water leaves blood, decrease in blood volume High concentration of electrolytes in blood Excessive water loss, sweating is shut-off Temperature rises rapidly (>40ºC) Heart failure