WOUTER VVSPARTiiFINALRS - Spiral
... However, without taking into account systemic and organ clearance of ...
... However, without taking into account systemic and organ clearance of ...
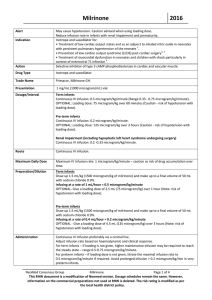
Milrinone 2016
... For term infants ─ if loading is not given, higher maintenance infusion may be required to reach the steady state – range 0.5-0.75 microgram/kg/minute. For preterm infants ─ if loading dose is not given, titrate the maximal infusion rate to 0.5 microgram/kg/minute if required. Avoid prolonged infusi ...
... For term infants ─ if loading is not given, higher maintenance infusion may be required to reach the steady state – range 0.5-0.75 microgram/kg/minute. For preterm infants ─ if loading dose is not given, titrate the maximal infusion rate to 0.5 microgram/kg/minute if required. Avoid prolonged infusi ...
Exercise Physiology - Anderson Training Systems
... Blood flow increases in proportion to the intensity of exercise but the blood flow patterns change rather markedly. Blood is redirected, away from areas where it is not essential, to areas that are active during the exercise. Only 15 to 20 percent of resting cardiac output goes to muscle. During exh ...
... Blood flow increases in proportion to the intensity of exercise but the blood flow patterns change rather markedly. Blood is redirected, away from areas where it is not essential, to areas that are active during the exercise. Only 15 to 20 percent of resting cardiac output goes to muscle. During exh ...
Ultrafiltration in Heart Failure - bcbsks.com
... (rehospitalization for heart failure, unscheduled office and emergency department visits) during follow-up. Results showed a weight loss of 5.0 versus 3.1 kg from baseline at 48 hours (p=0.001) for the ultrafiltration and usual care groups, respectively, with no difference in dyspnea scores between ...
... (rehospitalization for heart failure, unscheduled office and emergency department visits) during follow-up. Results showed a weight loss of 5.0 versus 3.1 kg from baseline at 48 hours (p=0.001) for the ultrafiltration and usual care groups, respectively, with no difference in dyspnea scores between ...
Pericardial Disease:
... The heart is held in place within the chest cavity by a sac that is called the pericardium. When patients have pericardial disease, fluid commonly accumulates within the pericardial sac. This fluid is referred to as pericardial effusion. When too much fluid accumulates around the heart, the increase ...
... The heart is held in place within the chest cavity by a sac that is called the pericardium. When patients have pericardial disease, fluid commonly accumulates within the pericardial sac. This fluid is referred to as pericardial effusion. When too much fluid accumulates around the heart, the increase ...
05Rates
... Selection also affects the evolutionary rate at the level of populations. For the most part, the only mutations that affect phylogenetics are those that are fixed in the population. Hence evolutionary rate is a combination of mutation rate and fixation rate. Fluctuations in population size, generation t ...
... Selection also affects the evolutionary rate at the level of populations. For the most part, the only mutations that affect phylogenetics are those that are fixed in the population. Hence evolutionary rate is a combination of mutation rate and fixation rate. Fluctuations in population size, generation t ...
Pericardial Disease:
... The heart is held in place within the chest cavity by a sac that is called the pericardium. When patients have pericardial disease, fluid commonly accumulates within the pericardial sac. This fluid is referred to as pericardial effusion. When too much fluid accumulates around the heart, the increase ...
... The heart is held in place within the chest cavity by a sac that is called the pericardium. When patients have pericardial disease, fluid commonly accumulates within the pericardial sac. This fluid is referred to as pericardial effusion. When too much fluid accumulates around the heart, the increase ...
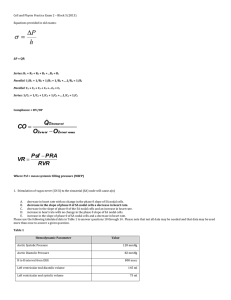
Optimization of axial-pump pressure sensitivity for a
... venous return (approximately 5 liters/min at rest). In addition, Figure 4 shows two other interesting points. First, systemic flow can be significantly reduced with an increase in peripheral vascular resistance (labeled “A”). Note that, at the low and high limits of the flow rates, the pressure sens ...
... venous return (approximately 5 liters/min at rest). In addition, Figure 4 shows two other interesting points. First, systemic flow can be significantly reduced with an increase in peripheral vascular resistance (labeled “A”). Note that, at the low and high limits of the flow rates, the pressure sens ...
Chapter 14: Autonomic Nervous System
... This sympathetic tone (vasomotor tone): Constricts blood vessels and causes blood pressure to rise as needed Prompts vessels to dilate if blood pressure is to be decreased ...
... This sympathetic tone (vasomotor tone): Constricts blood vessels and causes blood pressure to rise as needed Prompts vessels to dilate if blood pressure is to be decreased ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... stimulation except it lasts 5-10 times longer ...
... stimulation except it lasts 5-10 times longer ...
Mediastinum & peicardium
... Pericardial Sinuses • Two In number: – Lies within the pericardial cavity, at the points where the visceral and parietal pericardia are continuous with one another. – The pericardial sinuses are: • transverse pericardial sinus (Open “Connected Lt-Rt”) – Between the reflections of pericardium onto t ...
... Pericardial Sinuses • Two In number: – Lies within the pericardial cavity, at the points where the visceral and parietal pericardia are continuous with one another. – The pericardial sinuses are: • transverse pericardial sinus (Open “Connected Lt-Rt”) – Between the reflections of pericardium onto t ...
ELECTRONIC FETAL MONITORING (EFM
... • Speed of paper is usually 1cm per minute – hence I big square is 1 minute • The units used on the paper – 1 small square is 5 beats in the vertical axis • Sleeping cycle of fetus is 30 t0 40 mins – CTG should be done for atleast 20 to 30 mins- one can stimulate to awaken the baby like acoustic sti ...
... • Speed of paper is usually 1cm per minute – hence I big square is 1 minute • The units used on the paper – 1 small square is 5 beats in the vertical axis • Sleeping cycle of fetus is 30 t0 40 mins – CTG should be done for atleast 20 to 30 mins- one can stimulate to awaken the baby like acoustic sti ...
D - VCOMcc
... As venous return increases, force of contraction increases. As venous return increases, the stretch on the heart often exceeds optimal myofibril overlap. Increased venous return results in increased contractility by sympathetic stimulation. Increased venous return results in increased heart rate onl ...
... As venous return increases, force of contraction increases. As venous return increases, the stretch on the heart often exceeds optimal myofibril overlap. Increased venous return results in increased contractility by sympathetic stimulation. Increased venous return results in increased heart rate onl ...
File - Doctorswriting
... A. may fall to as little as -10 mmHg, but rarely more, at rest B. may be 6 cm of blood normally C. will tend to fall with venoconstriction D. increases with exercise E. increases with inspiration 59. Which of the following statements regarding cardiovascular regularity mechanisms is true A. The Cush ...
... A. may fall to as little as -10 mmHg, but rarely more, at rest B. may be 6 cm of blood normally C. will tend to fall with venoconstriction D. increases with exercise E. increases with inspiration 59. Which of the following statements regarding cardiovascular regularity mechanisms is true A. The Cush ...
Stress Echo - STA HealthCare Communications
... Doppler imaging and estimation of pulmonary artery pressures using tricuspid regurgitation velocity (It should be noted that patients with grade II or greater diastolic dysfunction at rest already have findings consistent with DHF and do not need to undergo DSE). Next, with continuous ECG monitoring ...
... Doppler imaging and estimation of pulmonary artery pressures using tricuspid regurgitation velocity (It should be noted that patients with grade II or greater diastolic dysfunction at rest already have findings consistent with DHF and do not need to undergo DSE). Next, with continuous ECG monitoring ...
Heart rate

Heart rate, or heart pulse, is the speed of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per unit of time — typically beats per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide. Activities that can provoke change include physical exercise, sleep, anxiety, stress, illness, ingesting, and drugs.The normal resting adult human heart rate ranges from 60–100 bpm. Tachycardia is a fast heart rate, defined as above 100 bpm at rest. Bradycardia is a slow heart rate, defined as below 60 bpm at rest. During sleep a slow heartbeat with rates around 40–50 BPM is common and is considered normal. When the heart is not beating in a regular pattern, this is referred to as an arrhythmia. These abnormalities of heart rate sometimes indicate disease.