Spike Train Decoding
... Spike rasters for a single neuron Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Trial 4 Trial 5 Time ...
... Spike rasters for a single neuron Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Trial 4 Trial 5 Time ...
Assignment 1 Help sheet
... There are many changes to the body during exercise; these can be classified as acute and chronic. Acute meaning they are short term and happen almost instantly with the onset of exercise. The other chronic is long term and allows the body to adapt its capabilities so therefore it can meet new demand ...
... There are many changes to the body during exercise; these can be classified as acute and chronic. Acute meaning they are short term and happen almost instantly with the onset of exercise. The other chronic is long term and allows the body to adapt its capabilities so therefore it can meet new demand ...
Cardio110-ExercisePhysI
... healthy system—exept at high exercise workloads. Sympathetic system is a stress response. Tends to be high in diseased states—stresses to the system. Plays role in progression of many cardiovascular diseases. When you Stop exercising: HR drops quickly. Most of initial decrease is return of paras ...
... healthy system—exept at high exercise workloads. Sympathetic system is a stress response. Tends to be high in diseased states—stresses to the system. Plays role in progression of many cardiovascular diseases. When you Stop exercising: HR drops quickly. Most of initial decrease is return of paras ...
Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... A small amount of work is required to impart kinetic energy to the heart (1/2 mV2). What is stroke-volume in previous figure? External work is area of Pressure-Volume curve. Work output is affected by “preload” (end-diastolic pressure) and “afterload” (aortic pressure). ...
... A small amount of work is required to impart kinetic energy to the heart (1/2 mV2). What is stroke-volume in previous figure? External work is area of Pressure-Volume curve. Work output is affected by “preload” (end-diastolic pressure) and “afterload” (aortic pressure). ...
1 Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... A small amount of work is required to impart kinetic energy to the heart (1/2 mV2). What is stroke-volume in previous figure? External work is area of Pressure-Volume curve. Work output is affected by “preload” (end-diastolic pressure) and “afterload” (aortic pressure). ...
... A small amount of work is required to impart kinetic energy to the heart (1/2 mV2). What is stroke-volume in previous figure? External work is area of Pressure-Volume curve. Work output is affected by “preload” (end-diastolic pressure) and “afterload” (aortic pressure). ...
A Contemporary Mission for Physical Education
... Types of stretching (ACSM, 2000) – Active: force of stretch provided by stretcher – Passive: force of stretch provided by partner – Static: slow sustained stretch held 10-30 sec, to mild discomfort – PNF (proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation): contractionrelaxation combination of movements us ...
... Types of stretching (ACSM, 2000) – Active: force of stretch provided by stretcher – Passive: force of stretch provided by partner – Static: slow sustained stretch held 10-30 sec, to mild discomfort – PNF (proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation): contractionrelaxation combination of movements us ...
ppt
... A small amount of work is required to impart kinetic energy to the heart (1/2 mV2). What is stroke-volume in previous figure? External work is area of Pressure-Volume curve. Work output is affected by “preload” (end-diastolic pressure) and “afterload” (aortic pressure). ...
... A small amount of work is required to impart kinetic energy to the heart (1/2 mV2). What is stroke-volume in previous figure? External work is area of Pressure-Volume curve. Work output is affected by “preload” (end-diastolic pressure) and “afterload” (aortic pressure). ...
slide_6
... A small amount of work is required to impart kinetic energy to the heart (1/2 mV2). What is stroke-volume in previous figure? External work is area of Pressure-Volume curve. Work output is affected by “preload” (end-diastolic pressure) and “afterload” (aortic pressure). ...
... A small amount of work is required to impart kinetic energy to the heart (1/2 mV2). What is stroke-volume in previous figure? External work is area of Pressure-Volume curve. Work output is affected by “preload” (end-diastolic pressure) and “afterload” (aortic pressure). ...
2 Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... A small amount of work is required to impart kinetic energy to the heart (1/2 mV2). What is stroke-volume in previous figure? External work is area of Pressure-Volume curve. Work output is affected by “preload” (end-diastolic pressure) and “afterload” (aortic pressure). ...
... A small amount of work is required to impart kinetic energy to the heart (1/2 mV2). What is stroke-volume in previous figure? External work is area of Pressure-Volume curve. Work output is affected by “preload” (end-diastolic pressure) and “afterload” (aortic pressure). ...
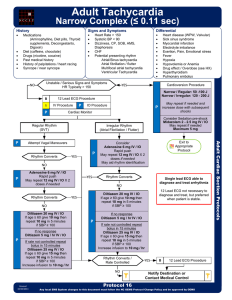
Adult Tachycardia
... Channel Blocker (e.g. Diltiazem) or Beta Blockers. Use caution with Adenosine and give only with defibrillator available. · Typical sinus tachycardia is in the range of 100 to (200 - patient’s age) beats per minute. · Regular Narrow-Complex Tachycardias: Vagal maneuvers and adenosine are preferred. ...
... Channel Blocker (e.g. Diltiazem) or Beta Blockers. Use caution with Adenosine and give only with defibrillator available. · Typical sinus tachycardia is in the range of 100 to (200 - patient’s age) beats per minute. · Regular Narrow-Complex Tachycardias: Vagal maneuvers and adenosine are preferred. ...
Protocol for Intermittent Auscultation
... Note: There is no research to indicate that a practitioner can determine the type of deceleration by using IA (eg. early, late). Therefore, decelerations cannot be further classified using intermittent auscultation. 2. Interpretation a. Reassuring i. Normal baseline FHR (110 to 160 bpm) ii. Presence ...
... Note: There is no research to indicate that a practitioner can determine the type of deceleration by using IA (eg. early, late). Therefore, decelerations cannot be further classified using intermittent auscultation. 2. Interpretation a. Reassuring i. Normal baseline FHR (110 to 160 bpm) ii. Presence ...
Exercise Physiology
... IN AEROBIC TRAINING, THE WORK DURATION IS OFTEN HIGH AND THE RELIEF IS LOW E.G. TIMED RUN FOR 1500M, WITH THE TIME TAKEN (E.G. 2MINS) GIVEN FOR REST (1:1 RATIO). IN ANAEROBIC TRAINING, THE WORK DURATION IS LOWER, BUT THE RELIEF IS HIGHER TO ALLOW FOR FULLER RECOVERY. E.G. SPRINT FOR 10SECS, THEN RES ...
... IN AEROBIC TRAINING, THE WORK DURATION IS OFTEN HIGH AND THE RELIEF IS LOW E.G. TIMED RUN FOR 1500M, WITH THE TIME TAKEN (E.G. 2MINS) GIVEN FOR REST (1:1 RATIO). IN ANAEROBIC TRAINING, THE WORK DURATION IS LOWER, BUT THE RELIEF IS HIGHER TO ALLOW FOR FULLER RECOVERY. E.G. SPRINT FOR 10SECS, THEN RES ...
How to train the cardiovascular patient
... What intensity of endurance training is recommended for cardiac patients? EACPR position paper: : • individualized approach after careful clinical evaluation • 150 min/week ideally 3–4 h/week Sub-maximal endurance training, • Start at 50% and gradually increasing to 50-70% of maximal HR • 50% HRmax ...
... What intensity of endurance training is recommended for cardiac patients? EACPR position paper: : • individualized approach after careful clinical evaluation • 150 min/week ideally 3–4 h/week Sub-maximal endurance training, • Start at 50% and gradually increasing to 50-70% of maximal HR • 50% HRmax ...
Case 1: W.C.
... these results in thehemodynamics context of all has peptide measurements to monitor available clinical andinought not to the be not been shown to be data helpful improving considered stand alone patient test. with HF outcomes of theahospitalized (ACC/AHA) 1Maisel ...
... these results in thehemodynamics context of all has peptide measurements to monitor available clinical andinought not to the be not been shown to be data helpful improving considered stand alone patient test. with HF outcomes of theahospitalized (ACC/AHA) 1Maisel ...
Advanced Heart Failure
... 5 Bristow MK. Management of heart failure. In: Braunwauld E, ed. Heart Disease: a Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. Vol 1. 6th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company, 2001:635-651 1 Russell, SD, Miller L, Pagani F. Advanced Heart Failure: A Call to Action. Circulation 2008. Publication Pending 2 ...
... 5 Bristow MK. Management of heart failure. In: Braunwauld E, ed. Heart Disease: a Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. Vol 1. 6th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company, 2001:635-651 1 Russell, SD, Miller L, Pagani F. Advanced Heart Failure: A Call to Action. Circulation 2008. Publication Pending 2 ...
The Multiphase Functional Cardiogram A Clinical
... Digital Signal Processing and ECG Analysis In a traditional 12-lead ECG, six limb and six precordial leads represent the vectors of the heart as an electrical power-generating source, reduced to a dipole with a pair of + & - signs. Conventionally, each lead is sampled at a rate of 200-500Hz, and the ...
... Digital Signal Processing and ECG Analysis In a traditional 12-lead ECG, six limb and six precordial leads represent the vectors of the heart as an electrical power-generating source, reduced to a dipole with a pair of + & - signs. Conventionally, each lead is sampled at a rate of 200-500Hz, and the ...
DOC - Gericareonline.net
... much exercise you can handle. If you can’t walk easily or safely, you can use an exercise bicycle for the test. While you are doing the test, you will be hooked up to equipment that monitors your heart beats and measures your blood pressure. You might also be asked to breath into a tube for a few mi ...
... much exercise you can handle. If you can’t walk easily or safely, you can use an exercise bicycle for the test. While you are doing the test, you will be hooked up to equipment that monitors your heart beats and measures your blood pressure. You might also be asked to breath into a tube for a few mi ...
CARDIOVASCULAR INTERACTIONS
... 1. Conservation of mass related to the difference between inflow, outflow and the accumulation of stressed volume in a compartment, using differencedifferential equations solved iteratively at 0.001 min intervals; 2. Distending Pressure related to stressed volume and compliance; 3. Flow related to p ...
... 1. Conservation of mass related to the difference between inflow, outflow and the accumulation of stressed volume in a compartment, using differencedifferential equations solved iteratively at 0.001 min intervals; 2. Distending Pressure related to stressed volume and compliance; 3. Flow related to p ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Welcome to Thrombo 360
... – Where there is a reversible cause – In heart failure caused by atrial fibrillation – In new-onset atrial fibrillation ...
... – Where there is a reversible cause – In heart failure caused by atrial fibrillation – In new-onset atrial fibrillation ...
Heart rate

Heart rate, or heart pulse, is the speed of the heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per unit of time — typically beats per minute (bpm). The heart rate can vary according to the body's physical needs, including the need to absorb oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide. Activities that can provoke change include physical exercise, sleep, anxiety, stress, illness, ingesting, and drugs.The normal resting adult human heart rate ranges from 60–100 bpm. Tachycardia is a fast heart rate, defined as above 100 bpm at rest. Bradycardia is a slow heart rate, defined as below 60 bpm at rest. During sleep a slow heartbeat with rates around 40–50 BPM is common and is considered normal. When the heart is not beating in a regular pattern, this is referred to as an arrhythmia. These abnormalities of heart rate sometimes indicate disease.