הצעה למבנה הקוריקולום לקורסים הקדם
... 1) Know the factors that determine the total energy of the flowing blood and the relationship among these factors. Describe the usual reference point for physiological pressure. 2) Be able to differentiate between flow and velocity in terms of units and concept. 3) Understand the relationship betwee ...
... 1) Know the factors that determine the total energy of the flowing blood and the relationship among these factors. Describe the usual reference point for physiological pressure. 2) Be able to differentiate between flow and velocity in terms of units and concept. 3) Understand the relationship betwee ...
Cardiac Qs
... permeability to calcium and sodium ions reduces the slope of the pacemaker potential. This response is faster to occur than sympathetic stimulation. Parasympathetic fibers also innervate the atria and the AV node where it increases the AV node delay. The action potential duration itself is lengthene ...
... permeability to calcium and sodium ions reduces the slope of the pacemaker potential. This response is faster to occur than sympathetic stimulation. Parasympathetic fibers also innervate the atria and the AV node where it increases the AV node delay. The action potential duration itself is lengthene ...
Paediatric shock
... Eventually however other compartments will also become depleted, as they are normally in physiological equilibrium with each other. A diagnosis of dehydration, by comparison, usually implies a more gradual, prolonged loss of fluid which comes from all fluid compartments. It is frequently associated ...
... Eventually however other compartments will also become depleted, as they are normally in physiological equilibrium with each other. A diagnosis of dehydration, by comparison, usually implies a more gradual, prolonged loss of fluid which comes from all fluid compartments. It is frequently associated ...
Sympathetic reflex compensations in shock
... Cardiac depression: when arterial blood pressure falls low enough, the myocardium itself gets damaged due to reduced blood supply in the coronaries. This weak heart muscle leads to further reduction in cardiac ...
... Cardiac depression: when arterial blood pressure falls low enough, the myocardium itself gets damaged due to reduced blood supply in the coronaries. This weak heart muscle leads to further reduction in cardiac ...
Irreversible shock
... Cardiac depression: when arterial blood pressure falls low enough, the myocardium itself gets damaged due to reduced blood supply in the coronaries. This weak heart muscle leads to further reduction in cardiac ...
... Cardiac depression: when arterial blood pressure falls low enough, the myocardium itself gets damaged due to reduced blood supply in the coronaries. This weak heart muscle leads to further reduction in cardiac ...
Cardiovascular homeostasis in health & disease
... • Understand the shock by discussing changes occurring in haemorrhagic shock. • Explain compensatory response of body to shock. • Identify the concept of irreversible (unresponsive) shock. ...
... • Understand the shock by discussing changes occurring in haemorrhagic shock. • Explain compensatory response of body to shock. • Identify the concept of irreversible (unresponsive) shock. ...
Shock - Doctors2Be
... • Type of distributive shock is neurogenic shock, in which there is sudden autonomic activity producing vasodilation, pooling of blood in the extremities, and fainting. These are called vasovagal attacks,. Other forms of syncope include – postural syncope, fainting due to pooling of blood in the dep ...
... • Type of distributive shock is neurogenic shock, in which there is sudden autonomic activity producing vasodilation, pooling of blood in the extremities, and fainting. These are called vasovagal attacks,. Other forms of syncope include – postural syncope, fainting due to pooling of blood in the dep ...
Fick Principle - 911 Training Concepts
... heart A major effect is the backup of blood into the lungs. Resulting buildup of pulmonary fluid is ...
... heart A major effect is the backup of blood into the lungs. Resulting buildup of pulmonary fluid is ...
Cardiovascular Physiology 2016
... • if SA node becomes damaged, AV node will take over but at a slower pace • if AV node becomes damaged, Bundle of His will take over but pace is too slow (28 bpm) and is not really compatible with life Ectopic Foci • abnormal conducting or contractile cells that generate AP’s and override the impuls ...
... • if SA node becomes damaged, AV node will take over but at a slower pace • if AV node becomes damaged, Bundle of His will take over but pace is too slow (28 bpm) and is not really compatible with life Ectopic Foci • abnormal conducting or contractile cells that generate AP’s and override the impuls ...
Bermingham, M
... RESULTS: The experimental group attained significant improvements over the control group in cardiovascular fitness, maximal workload, gait speed, and paretic lower-extremity muscle strength. The relatively short program (8 wk) of water-based exercise resulted in a 22% improvement in cardiovascular f ...
... RESULTS: The experimental group attained significant improvements over the control group in cardiovascular fitness, maximal workload, gait speed, and paretic lower-extremity muscle strength. The relatively short program (8 wk) of water-based exercise resulted in a 22% improvement in cardiovascular f ...
Practical CV_cardiac cycle
... The cardiac cycle and noninvasive methods of investigation - the carotidogram, the apexcardiogram, the jugulogramObjectives: I. The cardiac cycle: 1. Defining the concept 2. Parameters of the cardiac cycle 3. Phases of the cardiac cycle II. Non invasive methods for exploring the mechanical activity ...
... The cardiac cycle and noninvasive methods of investigation - the carotidogram, the apexcardiogram, the jugulogramObjectives: I. The cardiac cycle: 1. Defining the concept 2. Parameters of the cardiac cycle 3. Phases of the cardiac cycle II. Non invasive methods for exploring the mechanical activity ...
Hypovolemic Shock
... cause of hypovolemia. Vomiting and diarrhea from gastroenteritis is a second common cause. The signs and symptoms of hypovolemic shock vary with the amount, duration, and timing of fluid loss. As intravascular volume is further compromised by ongoing fluid losses (such as profuse diarrhea), the chil ...
... cause of hypovolemia. Vomiting and diarrhea from gastroenteritis is a second common cause. The signs and symptoms of hypovolemic shock vary with the amount, duration, and timing of fluid loss. As intravascular volume is further compromised by ongoing fluid losses (such as profuse diarrhea), the chil ...
One-and-a-Half Ventricular Repair through the Right Lateral
... verified, and no sinusoidal communications were observed. Diameters of the tricuspid and pulmonary valves were found to be 61% and 74%, respectively, of the anticipated normal values. These diameters corresponded to Z values of –4.6 and –3.1, respectively.2) We indicated a 1.5 VR for this patient as ...
... verified, and no sinusoidal communications were observed. Diameters of the tricuspid and pulmonary valves were found to be 61% and 74%, respectively, of the anticipated normal values. These diameters corresponded to Z values of –4.6 and –3.1, respectively.2) We indicated a 1.5 VR for this patient as ...
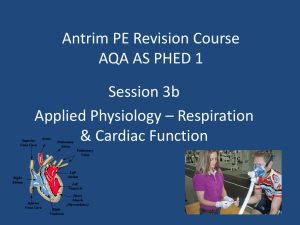
AQA PHED 1 Applied Physiology Respiration cardiac Function
... Cardiac cycle Cardiac output, stroke volume and heart rate and the relationship between them. Heart rate range in response to exercise; hormonal and nervous effects on heart rate; Role of blood carbon dioxide in changing heart rate Cardiac hypertrophy leading to bradycardia/athlete’s heart Starling’ ...
... Cardiac cycle Cardiac output, stroke volume and heart rate and the relationship between them. Heart rate range in response to exercise; hormonal and nervous effects on heart rate; Role of blood carbon dioxide in changing heart rate Cardiac hypertrophy leading to bradycardia/athlete’s heart Starling’ ...
Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
... minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
The Cardiac Output Curve
... minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
... minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
1 Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
... minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
CARDIAC ARRHYTHMIA
... tachycardia (AVNRT)- Junctionalarryhythmias These tachycardia are due to re-entry in a circuit involving AV node. It produces regular tachycardia with a rate of 120-240/min. Episode may last from few seconds to many hours ...
... tachycardia (AVNRT)- Junctionalarryhythmias These tachycardia are due to re-entry in a circuit involving AV node. It produces regular tachycardia with a rate of 120-240/min. Episode may last from few seconds to many hours ...
cardiac arrhythmia
... tachycardia (AVNRT)- Junctionalarryhythmias These tachycardia are due to re-entry in a circuit involving AV node. It produces regular tachycardia with a rate of 120-240/min. Episode may last from few seconds to many hours ...
... tachycardia (AVNRT)- Junctionalarryhythmias These tachycardia are due to re-entry in a circuit involving AV node. It produces regular tachycardia with a rate of 120-240/min. Episode may last from few seconds to many hours ...
2 Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle
... minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
... minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
slide_6
... minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
... minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
ppt
... minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
... minus end systolic volume (ESV) EDV = amount of blood collected in a ventricle during diastole ESV = amount of blood remaining in a ventricle after contraction ...
Heart Rate The interval between two successive R waves
... constant, but alternates between a systolic level (maximal blood pressure during the ejection phase = systolic blood pressure) and a diastolic level (minimal blood pressure at the late opening of the aortic valve = diastolic blood pressure). The systolic blood pressure normally is about 120 mmHg, th ...
... constant, but alternates between a systolic level (maximal blood pressure during the ejection phase = systolic blood pressure) and a diastolic level (minimal blood pressure at the late opening of the aortic valve = diastolic blood pressure). The systolic blood pressure normally is about 120 mmHg, th ...
Defibrillation

Defibrillation is a common treatment for life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias and ventricular fibrillation. Defibrillation consists of delivering a therapeutic dose of electrical energy to the heart with a device called a defibrillator. This depolarizes a critical mass of the heart muscle, terminates the dysrhythmia and allows normal sinus rhythm to be reestablished by the body's natural pacemaker, in the sinoatrial node of the heart.Defibrillators can be external, transvenous, or implanted (implantable cardioverter-defibrillator), depending on the type of device used or needed. Some external units, known as automated external defibrillators (AEDs), automate the diagnosis of treatable rhythms, meaning that lay responders or bystanders are able to use them successfully with little or no training at all.