* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Thoracic Wall
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
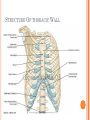
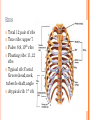
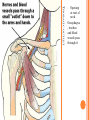
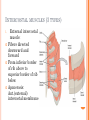
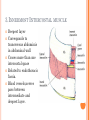
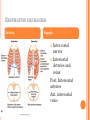
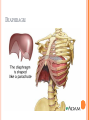
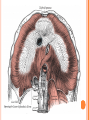
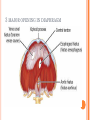
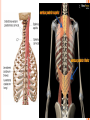
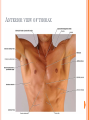
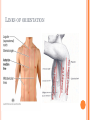
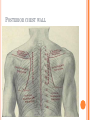
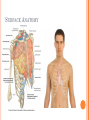
THORACIC WALL Benish Islam Lecturer / coordinator Surgical IPMS/KMU STRUCTURE OF THORACIC WALL STERNUM Manubrium Body of sternum: Manibriusternal joint Xipibhisternal joint Sternal angle Xiphoid process RIBS Total 12 pair of ribs True ribs: upper 7 False: 8,9,10th ribs Floating ribs: 11,12 ribs Typical rib:Costal Groove,head,neck, tubercle shaft,angle Atypical rib: 1st rib THORACIC OUTLET Opening at root of neck. Oesophagus , trachea and blood vessels pass through it • ENDOTHORACIC FASCIA Loose connective tissue Separate parietal pleura from thoracic wall INTERCOSTAL MUSCLES (3 TYPES) External intercostal muscle: Fibers directed downward and forward From inferior border of rib above to superior border of rib below Aponerosis: Ant.(external) intercostal membrane 1. 2. INTERNAL INTERCOSTAL MUSCLE Intermediate layer Fibers directed downward and backward From subcostal groove of rib above to upper border of rib below Aponeurosis: post. (internal) intercostal membrane 3.INNERMOST INTERCOSTAL MUSCLE Deepest layer Corresponds to transversus abdominis in abdominal wall Croses more than one intercostal space Related to endothoracic fascia. Blood vessels,nerves pass between intermediate and deepest layer. RESPIRATION MECHANISM: Action Supply Inter costal nerves Intercostal Arteries and veins: Post. Intercostal arteries Ant. intercostal veins DIAPHRAGM ORIGIN OF DIAPHRAGM Thin muscular tendinous septum,separate chest cavity above from abdominal cavity. Sternl part:arises from post. Surface of xiphoid process Costal Part:arise from deep surface of lower six ribs and costal cartilage. Verterbral part:arises from vertebral column nd arcuate ligament. Inserted into central tendon Rt.dome: upper border of 5th rib Lt. dome: lower border of5th rib DIAPHRAGM Nerve/Action Motor nerves: rt,lt. phrenic nerves C3,4,5 Sensory nerves: Phrenic nerve and lower six intercostal nerves Action:On contraction, diaphragm pulls down central tendon and inc. vertical diameter of thorax. Function Muscle of Inspiration Muscle of Abdominal Straining Weight lifting muscle Thoracoabdominal pump 3 MAJOR OPENING IN DIAPHRAGM ANTERIOR VIEW OF THORAX LINES OF ORIENTATION POSTERIOR CHEST WALL SURFACE ANATOMY THANK YOU