* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WELCOME TO THE WONDERFUL WORLD OF BACTERIA
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
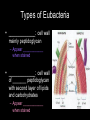
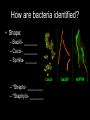
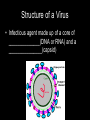
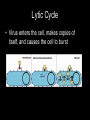
BACTERIA • ______________: single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus Bacterial Kingdoms (formerly Monerans) • Divided into TWO Kingdoms________________- “ancient bacteria” ________________- “good/true bacteria” ARCHAEBACTERIA • Characteristics – Most live in ___________________________ – Cell wall does _____ contain _____________ – DNA sequence similar to ________________ (possible ancestor?) Types of Archaebacteria • • • • • EXTREMOPHILES Methanogens- produce _________ Halophiles- live in ________ conditions Thermophiles- live in high ____________ Etc. EUBACTERIA • Live ______________________________ • Cell wall contains ___________________ • Wide array of characteristics Types of Eubacteria • ____________: cell wall mainly peptidoglycan – Appear ____________ when stained • ____________: cell wall of _______ peptidoglycan with second layer of lipids and carbohydrates – Appear ____________ when stained How are bacteria identified? • Shape: – Bacilli- _______ – Cocci- _______ – Spirilla- ______ – *Strepto- ________ – *Staphylo- _______ How are bacteria identified? • Cell Walls – Is peptidoglycans present? • Yes- ______________________ • No- _______________________ How are bacteria identified? • Movement – Some have ____________________ – Some glide, spiral, etc. – Others don’t move on own How are bacteria identified? • Energy obtaining methods – _____________________- make own food • _____________________- use light • _____________________- use inorganic materials – _____________________- take in food – _____________________- need light and a nutrient source How bacteria are identified? • Energy releasing processes: – Cellular respiration: requires Oxygen (__________________________) – Fermentation: no Oxygen used (___________________________) – Some can survive with or without oxygen (___________________________) How are bacteria identified? • Reproduction & Growth: – ____________________- double in size, replicates DNA, splits into two (asexual) Reproduction cont’d – ________________________- bridge forms between two cells and genes are transferred Conjugation – _____________________- thick wall around DNA can remain dormant until conditions are favorable VIRUSES • Virus- Latin for “_______________” • Smaller than bacteria • ___________ living! Structure of a Virus • Infectious agent made up of a core of ______________(DNA or RNA) and a _______________(capsid) Why not living? • Viruses can’t ___________ on their ownthey must use a host’s cells • Not made of ___________ • Cannot maintain _________________ Replication (Reproduction) • 2 Types of Replication: – __________ Cycle – __________ Cycle Lytic Cycle • Virus enters the cell, makes copies of itself, and causes the cell to burst Steps of Lytic Cycle – Virus attacks cell and ___________________ – DNA forms a circle Steps of Lytic Cycle cont’d – Viral DNA commands host cell to make __________________ Lytic Cycle Steps cont’d – Cell _____________ and releases viruses to invade more cells – *Symptoms of disease show Lysogenic Cycle • Virus embeds its DNA into the host’s DNA, both DNAs are replicated • ________________- viral DNA that is embedded into host’s DNA • *Symptoms of disease do not show at this time Types of Viruses • _____________- virus that infects bacteria Types of Viruses- cont’d • _____________- contain RNA as genetic code (HIV & AIDS, some cancer) RNA • _________________- cause cancer in animals (disrupt controls over cell growth) Not quite a virus, but… • ___________- “protein infectious particles” – Act like a virus, but… – Do not contain any ________, only ________ • Usually only affects _______________ • ___________– Act like a virus, but… – Has ________, but no ___________ • Usually only affects _________________ Protection from viruses- HOW? • PREVENTION! – Good hygiene – ______________- weakened or “killed” viruses or viral particle • Inject into body to build up immunity