* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the heart - Doktorscience
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
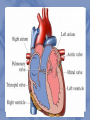
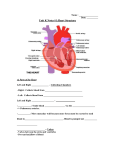
The Heart: Muscular organ located between lungs 32 000 000 beats per year! structure Composed of myocardium (cardiac muscle tissue) Inside the heart is lined with endocardium (squamous epithelial) Outside of heart is lined with pericardium which forms pericardial sac (for heart lubrication) The heart is divided into two halves by the septum Two halves of the heart are divided into 4 chambers Blood flow through the heart is controlled by valves The atrio-ventricular valves are held in place by chordae tendinae The semi lunar valves direct flow out of the heart (resemble a half moon) Function The heart acts as a double pump The right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs (called the pulmonary circuit) The left side pumps blood to the rest of the body (called systemic circuit) This is why the left side of the heart is larger (has to pump blood farther) Pathway of blood Venae cavae (inferior and superior) to the right atrium Right atrium to right ventricle Right ventricle to pulmonary artery (to lungs/pulmonary veins and back to heart) Left atrium to left ventricle Left ventricle to aorta to the body Systole – contraction: first atria contract, then ventricles Diastole – relaxation Sound: lub-dupp Lub: atrioventricular valves close Dupp: closing of semi-lunar valves Heart murmur often due to ineffective valves (hear a “slush” sound instead of “lub”) this can cause back-flow in the heart Blood pressure Average = 120/80 mm Hg systole of left ventricle diastole of left ventricle The ratio of the contraction and relaxations Heart beat control The heart beat is intrinsic, meaning it can beat independently of the central nervous system The heart has its own pacemaker: the sino-atrial node This is located in the upper dorsal wall of the right atrium The SA node initiates the heart beat by causing the atria to contract The electrical impulse then reaches the atrio-ventricular node located at the base of the right atrium The signal is then transmitted through the ventricles by purkinje fibres This then causes the ventricles to contract The heart is controlled by the nervous system at the medulla oblongota (brain stem) Heart beat is sped up or slowed down depending on what your body requires Electrocardiogram (ECG) shows voltage changes across the heart during contraction