* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The atrial walls are thinner than the ventricular walls. Higher
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
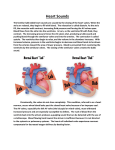
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
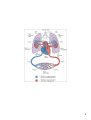
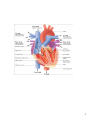
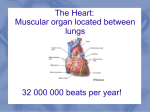
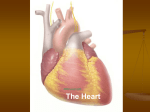
The heart has 4 chambers Heart Anato my an *separated so blood does not mix d B loodfl • Atria are divided by a wall called the interatrial septum • Ventricles are divided by the interventricular septum ow The atrial walls are thinner than the ventricular walls. Higher pressures are generated in the ventricles to move blood. Left ventricle walls are thicker than right ventricle walls (due to circuits they supply) 1 blav ian l. su Inferior vena cava – blood from the trunk, organs, abdomen, pelvic region, and lower extremities to the right atrium l. common carotid lic ha ep ioc ch Superior vena cava – blood from the head, neck, chest, and upper extremities to the right atrium bra Major Vessels Pulmonary veins bring blood back to the left atrium. Pulmonary trunk/artery carries blood from the right ventricle to the lungs. The aorta carries blood from the left ventricle to the body. 2 Valves of the Heart *one way , prevent backflow Atrioventricular (AV) valves – between each atrium and the ventricle on the same side • tricuspid valve right side • bicuspid valve, or mitral valve left side *Papillary muscles tense chordae tendineae: prevent valves from swinging into atria Semilunar valves – between the ventricles and the large arteries that carry blood away from the heart • The pulmonary semilunar valve right. • The aortic semilunar valve left. 3 Cardiac Cycle Cardiac cycle the period between the start of one heartbeat and the beginning of the next • Includes both contraction and relaxation Phases • Systole (contraction) chamber pumping • Diastole (relaxation) chamber filling Blood Pressure Rises during systole Falls during diastole Blood flows from high to low pressure • Controlled by timing of contractions • Directed by oneway valves Heart Rate At 75 beats per minute: Cardiac cycle lasts about 800 msecs When heart rate increases: All phases of cardiac cycle shorten, particularly diastole 4 Heart Sounds "Lub Dub" S1 Loud sounds (Lub) Produced by AV valves S2 Loud sounds (Dub) Produced by semilunar valves S3, S4 Soft sounds Blood flow into ventricles and atrial contraction 5 6 7