* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
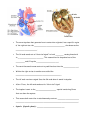
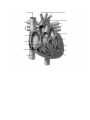
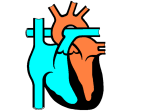
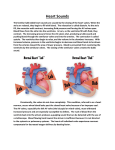
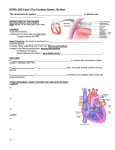
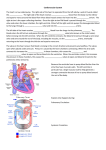
11.4 The Cardiac Cycle and Circulation The Heart is a specialized organ that pumps blood though the body In mammals, it is a 2-circuit system: 1) PULMONARY CIRCUIT – ___________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ 2) SYSTEMIC CIRCUIT–_____________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Location– it is situated ____________________________________________ Structure – the heart is enclosed in a sac, the _________, a two layered wall. The space between the two walls is a lubricating fluid that allows the walls of the heart to slide over one another as the heart beats without friction from other organs. Heart is composed mostly of ________________ – a muscle type that is exclusive to the heart only and has the ability to contract and relax quickly The heart has 4 chambers: Left atrium, Right atrium, Left ventricle, Right ventricle ATRIA The atria are ____________________________________________________ o Right atrium – receives blood from body o Left atrium – receives blood from lungs Cardiac muscle that lines the walls of atria is ______ because the atria responsible for pumping blood ________________________________________________ VENTRICLES Ventricles have a _________________ and have _________________ that are much more powerful than the atria. These thicker walls (especially left ventricle) pump blood _____________________________________________________ The left and right side of the heart are separated by the __________________ The pumping action of the heart is synchronized (happen at the same time on right and left side) Blood flows in one-way (always in the same direction) with the help of __________ that __________________________________________________________ Note: there are two types of valves: 1) atrioventricular valves (AV valves): _____________________________________ ______________________________________________________ 2) semilunar valves: ________________________________________ ______________________________________________________ Heart Beat / Cardiac Cycle Heart rate – ____________________________________________________ (measured by taking a pulse) During a single heart beat, or cardiac cycle, the heart is pumping twice - 2 contractions) Cardiac muscle is a myogenic muscle: it spontaneously ______________________ _________________________________; it doesn’t need the brain to control it! The nerve impulses that generate heart contraction originate from a specific region of the right atrium: the ______________________________, also known as the _____________________. The SA node sends out an “electrical signal” to both ________ causing them both to _________________________. This causes blood to be pushed out of the _________ and fill up the ______________________. The ventricles need to now contract to push blood out into the _______________. Within the right atrium is another area called the _____________________________________________ The AV node receives a signal from the SA node when it sends its impulse After 0.1 sec, the AV node sends out its “electrical” signal The impulse is sent to the ____________________: special conducting fibres that run down the septum This causes both ventricles to simultaneously contract, _____________________ ______________________________________________________________. Systole (Systolic phase) – ___________________________ Diastole (Diastolic phase) – ____________________________ Using a stethoscope, you can hear the characteristic hear sounds: “lub-dub, lubdub, lub-dub…” The “lub” sound is made by the closing of the atrioventricular valves (ventricular systole) The “dub” sound is made by the closing of the semilunar valves (ventricular diastole). CONTROL OF HEART RATE The heart mainly controls itself, however, the brain and hormones can influence the frequency of heart beats. During times of increased body activity (such as exercise), heart rate needs to increase to need demand for O2 by body cells and release accumulated CO2. The brain sends a signal to the adjust frequency accordingly. Hormones such as adrenaline (epinephrine) can also affect frequency Analysing the Heartbeat The cardiac cycle can be monitored using an ______________________ which measures electrical signals and produces an _________________________ (ECG)