* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart Sounds/Disorders
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
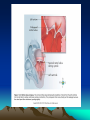
Objectives • 1. Discuss heart sounds • 2. Describe the major types of cardiac valve disorders • 3. Explain how a myocardial infarction might occur. • 4. Describe the major types of cardiac dysrhythmia. • 5. List and describe possible causes of heart failure. Heart Sounds • Two distinct sounds can be heard when listening to the heart – “lub dup” • “lub” – caused by vibration and abrupt closure of the AV valves as the ventricle contracts • This sound is of a longer duration and lower pitch than is the second sound. • “dup” – closing of the semilunar valves Valve Disorders • Incompetent valves – leak • Stenosed valves – narrower than normal • Rheumatic heart disease – inflammation of cardiac valves and other tissues • Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) – bicuspid valve flaps extend into left atrium causing incompetence Heart Attack • A myocardial infarction may result from occlusion or blockage of the left coronary artery Cardiac Dysrhythmia • Heart block – AV node block • Bradycardia – slow heart rhythm (below 60 beats per minute); slight bradycardia is normal during sleep; abnormal caused from improper autonomic nervous control of the heart or a damaged SA node • Tachycardia – rapid heart rhythm (over 100 beats per minute); normal during exercise or stress response; abnormal results from improper autonomic control of the heart, blood loss or shock, action of drugs and toxins, fever, et al • Sinus dysrhythmia – variation in heart rate during breathing cycle Extrasystoles • Frequent premature contractions • Can lead to fibrillation – cardiac muscle fibers contract out of step with each other • Ventricular fibrillation – immediately lifethreatening Heart Failure • Cardiomyopathy – disease of the myocardial tissue, reduces pumping effectiveness • Dysrhythmias can impair pumping effectiveness • Congestive heart failure – left heart failure; decreases pumping pressure in the systemic circulation (portions become congested with fluids)