* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 18
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
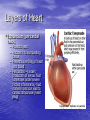
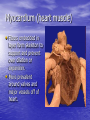
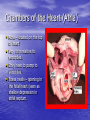
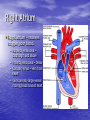
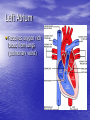
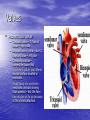
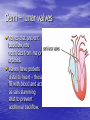
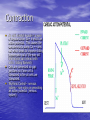
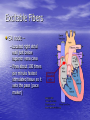
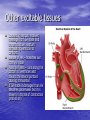
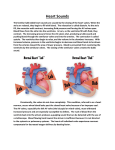
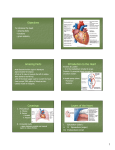
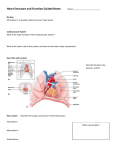
Chapter 18 Circulatory System Heart (general) • Size of a fist • Almost one pound in • • weight Middle of chest points to left Just superior to zyphoid process Layers of Heart • Epicardium (pericardial sack) – Protects heart – Anchors it to surrounding tissue – Prevents overfilling of heart with blood – Pericarditis – hinders production of serous fluid sometimes under severe friction inflammatory fluid rushes in and can lead to cardiac tamponade (heart plug) Myocardium (heart muscle) • Fibers embedded in • layer form skeleton to support and prevent over dilation or expansion. More prevalent around valves and major vessels off of heart. Endocardium • Thin tissue layer which lines the inside of the heart. Chambers of the Heart (Atria) • Atria – located on the top • • • of heart Very thin relative to ventricles. Only have to pump to ventricles. Fossa ovalis – opening in the fetal heart (seen as shallow depression in atrial septum. Right Atrium • Right atrium – receives oxygen poor blood. – superior vena cava – diaphragm and above – inferior vena cava – below – Coronary sinus – vein from heart – Veins are any large vessel moving blood toward heart. Left Atrium • Receives oxygen rich blood from lungs (pulmonary veins) Ventricles • Located on the bottom • Right ventricle lies toward • • • the front Left ventricle lies towards the back (largest and most muscular chamber) Septum – portion that divides the left from the right chambers Sulcus – groove formed between atria and ventricles Circulatory Circuit • Pulmonary circuit – right • • side Systemic circuit – left side Coronary circuit – feeds the heart to thick for diffusion – blockages or narrowing of these vessels can be fatal if not corrected (bi – pass) Valves • Atioventricular valves – Tricuspid valve – 3 flaps of tissue – right side – Bicuspid valve (mitral valve) 2 flaps of tissue – left side – Chordae tendinae – connective tissue that attaches to valves and inferior muscle surface located in ventricles. – Blood flows into ventricles ventricles contract shoving flaps upward – but the flaps can only go so far up because of the chords attached. Semi – lunar valves • Valves that prevent • backflow into ventricles from major arteries. Valves have pockets distal to heart – these fill with blood and act as sails slamming shut to prevent additional backflow. Contraction • As with skeletal muscle – a wave • • of depolarization Na+ in elicits an action potential. This causes the sarcolemma to dump Ca ++ ions out which binds to troponin sliding tropomyosin out of the way sot that myosin can interact with actin. (sliding filament) Cells are connected via gap junctions so if one cell is stimulated to fire all cells are stimulated. Rhythmic Control – nervous system – see notes on generating an action potential (nervous system) Excitable Fibers • SA node – – Located right atrial wall just below superior vena cava – Fires about 100 times per minute fastest stimulated tissue so it sets the pace (pace maker) Other excitable tissues • Located in septum receives message from SA node and transmits down septum stimulating ventricle to contract • Bundle of His – branches out from AV node • Purkinje fivers – runs along the bottom of ventricles and toward the lateral portions causing stimulation. • If SA node is damaged than AV becomes pacemaker but it is slower in its rate of contraction (and so on) EKG / ECG electrocardiogram • P wave – atrial • • depolarization QRS complex – ventricle depolarization T wave – ventricle repolarization