* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Orbitals and Quantum Numbers
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Measurement in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Spin (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Quantum entanglement wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Quantum dot wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Many-worlds interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum fiction wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Quantum computing wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
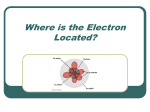
Orbitals and Quantum Numbers Objective Students will be able to describe the quantum numbers n, l, and ml used to define an orbital in an atom, and list the limitations placed on the values each may have. What is an orbital? An orbital is an allowed energy state of an electron in the quantum-mechanical model of the atom; the term orbital is also used to describe the spatial distribution of the electron. Defined by the values of 3 quantum numbers: n, l, and ml 4 Quantum Numbers (reminder: quantum numbers specify the properties of atomic orbitals and the properties of electrons in orbitals) 1) The principle quantum number (n) indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron n can have integral values of 1, 2, 3, etc. 2) the angular momentum (or azimuthal) quantum number (symbolized by l ) indicates the shape of the orbital l can take on integral values from 0 to n-1 for each value of n Value of l 0 1 2 3 letter used s p d f 3) the magnetic quantum number (ml) describes the orientation of the orbital in space It can take on values from l to –l 4) Electron Spin Quantum Number (ms) This number indicates the two fundamental spin states of an electron in an orbital This quantum number can only have two possible values, +1/2 or -1/2 Pauli Exclusion Principle – states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of 4 quantum numbers n, l, ml, and ms Practice Problem 1) For n=4, what are the possible values of l ? Answer l = 0,1,2,3 (what do these values correspond to?) Practice Problem #2 For l =2, what are the possible values of ml ? Answer ml = 2,1,0,-1,-2 (what do these values correspond to?) Practice Problem #3 State whether the following is a permissible set of quantum numbers for an electron in a hydrogen atom: n=2, l = 1, ml = 1 Answer Yes, it’s permissible (2p)