* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classifying Chemical Reactions 9-3
Host–guest chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Determination of equilibrium constants wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
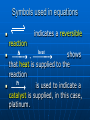
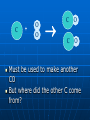
Unit 4: Toxins Intro Chemistry Chemical Toxins Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes that it undergoes. We have learned about how chemical compounds are formed We have also learned the language of chemistry, chemical formulas Certain chemicals interact with the human body in a negative way and are known as toxins Now we will equations for chemical reactions to learn about toxic substances. Keeping Track of Atoms Law of Conservation of Matter Conservation of Matter: in all chemical and physical changes, matter is neither created or destroyed • The total mass in a chemical reaction remains constant Antoine Lavoisier: • Made accurate and precise measurements during chemical reactions • Found that the total mass at the beginning = total mass at end of reaction Chemical Reactions A chemical change is really a chemical reaction Has two parts: • Reactants: the substances you start with • Products: the substances you end up with The reactants turn into the products 4 Fe + 3 O2 2 Fe2O3 Reactants products Ways to Express a Chemical Reaction The way atoms are joined is changed in a chemical reaction. Can be described several ways: 1. In a sentence Copper reacts with chlorine to form copper (II) chloride. 2. In a word equation Copper + chlorine copper (II) chloride 3. In chemical formulas: Cu + Cl2 CuCl2 Symbols in equations the arrow separates the reactants from the products (s) or after the formula = solid (g) or after the formula = gas (l) after the formula = liquid (aq) after the formula - dissolved in water, an aqueous solution Symbols used in equations reaction indicates a reversible shows that heat is supplied to the reaction Pt is used to indicate a catalyst is supplied, in this case, platinum. heat , What is a catalyst? A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a reaction, without being changed or used up by the reaction. Enzymes are biological or protein catalysts. Skeleton and Balanced Equations Use formulas and symbols to describe a reaction Don’t indicate how many of each element/compound Balanced equations: the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the reaction. Use coefficients to balance equation Coefficients and Subscripts Coefficients: large whole numbers placed in front of formula which represents number of units of that compound Subscript: small whole number placed in chemical formula to represent number of atoms of an element in a compound 4 Fe + 3 O2 Coefficient 2 Fe2O3 subscript Study Buddy Review What is the Law of Conservation of mass? What does the symbol (l) mean? What does (aq) mean? What is a coefficient? What is a subscript? How to Balance Chemical Equations Balanced Equation A balanced equation has the same number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation Atoms can’t be created or destroyed All the atoms at the beginning must appear in the end C + O O C O C + O2 CO We need one more oxygen in the products. Can’t change the formula, because it describes what it is (carbon monoxide in this example) C + O O C O C O Must be used to make another CO But where did the other C come from? C + C O O C O C O Must have started with two C 2 C + O2 2 CO Rules for balancing: Assemble, write the correct formulas for all the reactants and products Count the number of atoms of each type of element appearing on both sides Balance the atoms of an element one at a time by adding coefficients (the numbers in front) - save H and O until LAST! Check to make sure it is balanced. Never change a subscript to balance an equation. • If you change the formula you are describing a different reaction. • H2O is a different compound than H2O2 Never put a coefficient in the middle of a formula • 2 NaCl is okay, Na2Cl is not. Balancing Equations Examples H2 (g) + O2 (g) Zn + Pb (NO3)2 + HCl H2O (l) H2 + K2S ZnCl2 PbS + KNO3