* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice Final P132 Spring 2004 9:30 section
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
History of subatomic physics wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
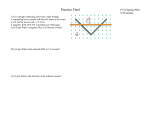
Practice Final P132 Spring 2004 9:30 section 1) Two straight conducting rails form a right triangle. A conducting bar in contact with the rails starts at the vertex at t=0. the bar moves with v=5.2 m/s. A magnetic field, B=0.35T is pointing out of the page. 1a) (10 pts) What is magnetic flux as a function of time? 2b) (10 pts) What is the induced EMF at t=5 seconds? See LECTURE NOTES CH 31, page 8 for solution 3c) (5 pts) What is the direction of the induced current? Multiple choice are 5 pts each 2) Two point charges Qa and Qb are placed a distance d apart. The electric field is zero at a point P between the charges on a line segment connecting them. Which of the following is true? a) Qa and Qb must have the same magnitude and sign. b) Qa and Qb must have the same magnitude but different sign. c) P must be midway between the two charges d) Qa and Qb can have different magnitudes but must have the same sign. e) Qa and Qb can have opposite signs but must have the same magnitude. 3) Two small charged objects attract each other with a force F when separated by a distance d. If the charge on each object is reduced to 1/3 of its original value and the distance is reduced to 1/3its original value the new force becomes: a) F b) F/3 c) F/9 d) F/18 e) F/27 4) two wires are made out of different material but they have the same current density. They carry the same current if: a) their lengths are the same b) their cross sectional areas are the same c) their lengths and cross sectional areas are the same d) the electric field inside the wire is the same e) the potential difference across the wires are the same 5) Which of the following is true if the charge on a parallel plate capacitor is doubled? a) the capacitance decreases by half b) the capacitance increases by 2 c) the electric field is halved d) the electric field is doubled e) and c are true 6) The magnetic force is parallel to the velocity vector of a charged particle when a) the particle is moving parallel to the magnetic field b) the particle is moving perpendicular to the magnetic field c) the particle is moving anti-parallel to the magnetic field d) never 7) A long wire of radius a is inside and concentric to a metal cylinder of inner radius b and outer radius c as shown in the diagram. A current 2I, into the page, is running in the wire and a current 6I running out of the page in the cylinder. Answer the following: a) (10 pts) What the magnetic field in the region r<a? B= µ 0 Ir πa 2 b) (10 pts) What is the magnetic field in the region a<r<b? B= µ0 I πr c) (5 pts) What is the magnetic field in the region r>c? B= 2µ 0 I πr c b a 8) (25 pts) Use the Biot-Savart law to show that the magnitude of the magnetic field at point P is: B= µ I B= 0 4π ∫ µ 0i 2 8πa dl × r r3 µ I = 0 4π ∫ dl sin θ r2 µ I = 0 4π a adl ∫r 0 3 a µ Ia dl = 0 2 2 3/ 2 4π ( l + a ) 0 ∫ Use integral #19 in appendix a a µ Ia µ 0 Ia µ0 I 2 dl l = = B= 0 2 2 3/ 2 8πa 4π 4π a 2 (l 2 + a 2 )1/ 2 0 + ( l a ) 0 ∫ 9) (25 pts) The following is a cross section of cylindrical capacitor of length L. A positive charge +Q is on the inner conductor (radius a) while –Q is on the outer conductor (radius b). Show that the capacitance is given by: C= 2πε 0 L ln(b / a ) See textbook page 592-593 b a 10) ) In the following circuit E=10V, R1=20Ω and R2=R3=R4=12Ω. a) (10 pts) What is the current through each resistor? I1=(10/24)A = 0.42A current through other three resistors is I1/3=0.14A b) (5pts) What is the voltage drop across each resistor ? Use V=IR V1=(10/24)(20Ω)=8.3Volts V2=V3=V4=(0.14)(12Ω)=1.7V c) (5pts) What is the equivalent resistance of this circuit? 24Ω d) (5 pts) How much power is dissipated in R1? P=(0.42)2(20Ω)=3.5W 11) Suppose instead of resistors we have only capacitors in the circuit. In the place of R1we have a 15µF capacitor and the other three capacitors have value of 5µF. a) (10 pts) What is the equivalent capacitance of the circuit? C=7.5µF b) (10 pts) What is the charge on each capacitor? Q1=(5V)(15µF)=75µC Q2=Q3=Q4=(5V)(5µF)=25µC c) (5 pts) What is the voltage drop across each capacitor? (Easier to do part c before b) 5V Multiple choice are 5 pts each 12) A uniform magnetic field is into the page. A charged particle moving in the plane of this page follows a clockwise spiral of increasing radius. One explanation is: a) the charge is positive and the particle is slowing down. b) the charge is negative and the particle is slowing down. c) the charge is positive and the particle is speeding up. d) the charge is negative and the particle is speeding up. e) none of the above. 13) If two or more capacitors are in series then: a) the charge on each capacitor is always the same. b) the voltage across each capacitor is always the same. c) the energy in each capacitor is always the same. d) the magnetic field in each capacitor is always the same. 14) A solid conducting sphere has 10 C of excess charge on it. a) The electric field at all points inside the sphere is zero. b) The electric potential increases as we move from the center of the sphere to its outside surface. c) The electric field is zero everywhere outside the sphere. d) The electric potential is zero everywhere outside the sphere. 15) The charge at a certain point in a circuit is changing according to: q(t)=5+3t2 (Coulombs) what is the current at t=5 seconds? a) 30A b) 80A c) 130A d) 150A 16) A wooden stick 2 m long is held in an uniform electric field that is parallel to the stick of 200 N/C. The potential difference between the ends of the stick is: a) 0V b) 100V c) 200V d) 400V







![[ ] ò](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003342726_1-ee49ebd06847e97887fd674790b89095-150x150.png)