* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Haber - Sra. Gibson
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Germanic weak verb wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chichewa tenses wikipedia , lookup
Sotho verbs wikipedia , lookup
Germanic strong verb wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Hungarian verbs wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Latin conjugation wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Grammatical tense wikipedia , lookup
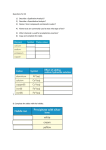
Haber To have To Have • The verb “to have” is used in three different ways in English: – to have something (possession) – to have to do something (obligation) – to have done something (reference to an activity) • Consider the following examples: – I have a wagon. – I have to study for a test. – I have been to the zoo. Tener vs. Haber • Tener is used to talk about possession and obligation. • Haber is used to refer to actions. – Haber can be confusing at first, but mastering it is a big step toward mastering Spanish. – Tenses that use haber are referred to as perfect tenses. Using “to have” to talk about actions • • • • I have seen that movie. I would have spoken to her. I will have graduated by then. I had been waiting for an hour. Haber • Haber can be conjugated into any tense, just like any other verb. • Present (he, has, ha…), Preterit (hube, hubiste, hubo…), Imperfect (había, habías, había…), etc. • However, haber never stands alone. It is always accompanied by another verb, in the past participle form. (See next slide) • Haber is irregular in many tenses. Past Participle • The past participle of a verb is formed by removing the ending (–ar, –er, or –ir) and adding –ado (for –ar verbs) or –ido (for –er or –ir verbs). • When used with haber, the participles are not modified according to number or gender. • There are many irregular past participles. Present Perfect • This is where things get a little confusing. The present perfect is used to talk about things that have happened, meaning that it actually refers to the past; however, the present tense of haber is used. (This same confusion exists in English, we just don’t ever think about it.) – Yo he hablado con ella. Present yo form of haber. Past participle of haber – I have spoken to her. Haber in different Tenses Present he hemos has ha Preterit hube Imperfect hubimos hubiste han hubo I have talked to her. Yo he hablado con ella. hubieron I had talked to her. Yo hube hablado con ella. (This is very uncommon; the imperfect is generally used instead.) habríamos habrías habría había I would have talked to her. Yo habría hablado con ella. habían I had talked to her. Yo había hablado con ella. Future habré habremos habrás habrían habíamos habías Conditional habría había habrá habrán I will have talked to her. Yo habré hablado con ella. Practice • Using what you have just learned, try to translate the following sentences: – I have eaten dinner. – You have visited your friends. – We had already arrived. – He would have made good grades. – They will have called already.