* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Guide to Operating System Security
Multilevel security wikipedia , lookup
Post-quantum cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Airport security wikipedia , lookup
Antivirus software wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Computer virus wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Security Essentials wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Next-Generation Secure Computing Base wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
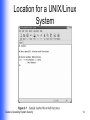
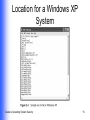
Guide to Operating System Security Chapter 2 Viruses, Worms, and Malicious Software Learning Objectives Explain how viruses, worms, and Trojan horses spread Discuss typical forms of malicious software and understand how they work Use techniques to protect operating systems from malicious software and to recover from an attack Guide to Operating System Security 2 Viruses, Worms, and Trojan Horses Different forms of malicious software (malware) Intended to Cause distress to a user Damage files or systems Disrupt normal computer and network functions Guide to Operating System Security 3 Viruses Programs borne by a disk or a file that has the ability to replicate Typically affect Executable program Script or macro Boot or partition sector of a drive Guide to Operating System Security 4 How Viruses Spread Transported from one medium or system to another Replicated throughout a system (eg, W32.Pinfi) Guide to Operating System Security 5 Virus Classification (Continued) How they infect systems Boot or partition sector File infector Macro Multipartite Guide to Operating System Security 6 Virus Classification (Continued) How they protect themselves from detection or from a virus scanner Armored Polymorphic Stealth Companion Benign or destructive Guide to Operating System Security 7 Worms Programs that replicate on the same computer or send themselves to many other computers Can open a back door Guide to Operating System Security 8 How Worms Spread Buffer overflow (eg, Code Red and Code Red II) Port scanning or port flooding Compromised passwords Guide to Operating System Security 9 Trojan Horses and How They Spread Programs that at first appear useful, but can cause damage or provide a back door Examples Backdoor.Egghead AOL4FREE Simpsons AppleScript Virus Guide to Operating System Security 10 Locations for Viruses, Worms, and Trojan Horses (Continued) Guide to Operating System Security 11 Locations for Viruses, Worms, and Trojan Horses (Continued) Guide to Operating System Security 12 Locations for Viruses, Worms, and Trojan Horses (Continued) Guide to Operating System Security 13 Location for a UNIX/Linux System Guide to Operating System Security 14 Location for a Windows XP System Guide to Operating System Security 15 Typical Methods Used by Malicious Software Executable methods Boot and partitions sector methods Macro methods E-mail methods Software exploitation Spyware Guide to Operating System Security 16 Executable Methods Files that contain lines of computer code that can be run Examples: .exe, .com, .bat, .bin, .btm, .cgi, .pl, .cmd, .msi Can infect source or execution code of a program Guide to Operating System Security 17 Boot and Partition Sector Methods Particularly affect Windows and UNIX systems Typically infect/replace instructions in MBR or Partition Boot Sector Can corrupt address of primary partition May move boot sector to another location if size of virus exceeds space allocated for boot sector Eradication typically involves recreating MBR and Partition Boot Sector instructions Guide to Operating System Security 18 Macro Methods A virus can infect a macro and spread each time the macro is used Software is configured so that macros are disabled unless digitally signed by a trusted source Guide to Operating System Security 19 Macro Protection Guide to Operating System Security 20 E-Mail Methods Sent as attachments to e-mail Guide to Operating System Security 21 Software Exploitation Particularly aimed at new software and new software versions Examples of potential vulnerabilities DNS services Messaging services Remote access services Network services and applications Guide to Operating System Security 22 Spyware Software placed on a computer typically without user’s knowledge reports back information about user’s activities Some operate through monitoring cookies Guide to Operating System Security 23 Protecting an OS from Malicious Software Install updates View what is loaded when a system is booted Use malicious software scanners Use digital signatures for system and driver files Back up systems and create repair disks Create and implement organizational policies Guide to Operating System Security 24 Installing Updates for Windows Windows Update Provides access to patches that are regularly issued Service packs Address security issues and problems affecting stability, performance, or operation of features included with the OS Guide to Operating System Security 25 Using Windows Update Guide to Operating System Security 26 Using Windows Update Guide to Operating System Security 27 Installing Updates for Red Hat Linux (Continued) Issued frequently; can be downloaded from Web site Red Hat Network Alert Notification Tool must be configured Guide to Operating System Security 28 Installing Updates for Red Hat Linux (Continued) Guide to Operating System Security 29 Installing Updates for NetWare Download updates and/or consolidated support packs from Novell’s Web site Guide to Operating System Security 30 Installing Updates for Mac OS X Software Update tool enables you to: Configure the system to automatically check for updates at specified intervals Manually check for updates View currently installed updates Guide to Operating System Security 31 Installing Updates for Mac OS X Guide to Operating System Security 32 Viewing What Is Loaded When a System Is Booted Windows 2000, Windows XP Professional, and Windows Server 2003 Red Hat Linux and NetWare View information on-screen Have a log record information (Advanced Options menu) Automatically display boot load information Mac OS X Display boot process by booting into either single user mode or verbose mode Guide to Operating System Security 33 Advanced Options Menu Guide to Operating System Security 34 Using Malicious Software Scanners Effective way to protect operating system Scan systems for virus, worms, and Trojan horses Often Called Virus Scanners Guide to Operating System Security 35 Malicious Software Scanners: Features to Look For (Continued) Scans memory and removes viruses Continuous memory scanning Scans hard and floppy disks and removes viruses Scans all know file formats Scans HTML documents and e-mail attachments Guide to Operating System Security 36 Malicious Software Scanners: Features to Look For (Continued) Automatically runs at a scheduled time Manual run option Detects known and unknown malicious software Updates for new malicious software Scans files that are downloaded Uses protected or quarantined zones for downloaded files Guide to Operating System Security 37 Using a Virus Scanner Guide to Operating System Security 38 Virus Scanning Software (Continued) Guide to Operating System Security continued… 39 Virus Scanning Software (Continued) Guide to Operating System Security 40 Using Digital Signatures for System and Driver Files Digital signature Code placed in a file to verify its authenticity by showing that it originated from a trusted source Driver signing Placing a digital signature in a device driver to • Show that the driver is from a trusted source • Indicate compatibility with an OS Guide to Operating System Security 41 Backing Up Systems and Creating Repair Disks Most OSs offers ways to back up your system Some OSs enable creation of a boot disk or repair disk Windows 2000 • Emergency Repair Disk (ERD) Windows XP or Windows Server 2003 • Automated System Recovery (ASR) set Red Hat Linux • Boot disk Guide to Operating System Security 42 Creating a Windows 2000 ERD Create a new ERD each time you: Install software Make a server configuration change Install a new adapter Add a NIC Restructure a partition Upgrade the OS Enables you to fix problems with the server Guide to Operating System Security 43 Creating a Windows 2000 ERD Guide to Operating System Security 44 Creating an ASR Set Two components Backup of all system files (1.5 MB or more) Backup of system settings (about 1.44 MB) Does not back up application data files Guide to Operating System Security 45 Creating an ASR Set Guide to Operating System Security 46 Creating a Red Hat Linux Boot Disk Enables booting a system from a floppy disk Guide to Operating System Security 47 Creating and Implementing Organizational Policies (Continued) Provide users with training in security techniques Train users about common malicious software Require users to scan floppies and CDs before use Establish policies about types of media that can be brought in from outside and how they can be used Establish policies that discourage/prevent users from installing their own software Guide to Operating System Security 48 Creating and Implementing Organizational Policies (Continued) Define policies that minimize/prevent downloading files; require users to use a virus scanner on any downloaded files Create quarantine areas for files of uncertain origin Use virus scanning on e-mail and attachments Discard e-mail attachments from unknown or untrusted sources Guide to Operating System Security 49 Chapter Summary Viruses, worms, and Trojan horses Typical forms of malicious software How they spread through operating systems and across networks What they target and why Boot sector viruses Viruses that attack through macros How to set up defenses, such as operating system patches and repair disks Guide to Operating System Security 50