* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Birth of Islam - HISTORY APPRECIATION
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic extremism in the 20th-century Egypt wikipedia , lookup
Gender roles in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Abbasid Caliphate wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
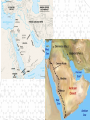
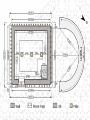
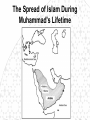
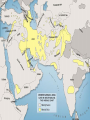
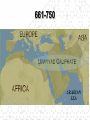
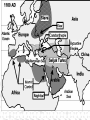
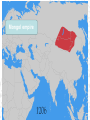
The Birth of Islam Arab rise to Power Arab Culture • Arabian Peninsula (Desert) • Bedouin existence (nomadic) • Loyalty & identification with tribes & clans – Necessary for protection and survival • Oasis towns, Animal Husbandry, Trade – Trade with Persia, Byzantines, India – Camel indigenous Scarce resources conflict – Rivalry over available water – Differing degrees of wealth • Polytheistic deities (Ka'aba at Mecca) • Oral Traditions – Poetry – source of unity & identity Ka’aba MuhaMMad’s Life & iMpact • Merchant of the Quraysh clan • Khadijah (wife of Muhammad) • Respected, worked as intermediary between rival clans • Vision of Angel Gabriel, one God, Allah – Followers small in number at first, grew overtime – Viewed as a threat by Umayyad clan as his influence grew – Forced to flee Mecca for Medina (hejira) in 622 • By 632, most of Peninsula, included the Umayyad were won over to the new faith The Spread of Islam During Muhammad's Lifetime Tenants of the Faith: the Five Pillars • One God – Allah, Muhammad is the prophet • Prayer towards Mecca 5x a day (salat) • Tax for Charity (zakat) • Fasting during the Holy Month of Ramadan • Pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj) Spread of Islam Spread of Islam Abu Bakr succeeded Muhammad established Caliph-completed the unification of the Arabs of the peninsula. •Under the first four Caliphs Islam spread into the Levant, Mesopotamia, Persia and Egypt •At the death of the Fourth Caliph, Ali, conflict emerged as to the rightful successor. sunni & shi’ite (shia) spLit • Dispute as to the rightful successor Sunni Chosen by followers (Caliph) Majority Shia Descendants of Muhammad (Imam) Minority • Civil War • Umayyad (Sunni Muslim) -military prowess brought combative followers under their control Umayyad Caliphate 661-750 Abbasid Caliphate Reached Peak of golden Age under Harun al-Rashid (786-809) Islamic Caliphates Umayyad Caliphate • Hereditary succession @ Damascus • Conquered -parts of Byzantine, collapsed Sassanid Persians, Hindu Kingdom (Sind) Abbasid Caliphate • Founders - More cosmopolitan – Persians, Egyptians, Mesopotamians held high positions in government • Capital at Baghdad – walled city – 100,000’s people Est. Dar al-Islam • Tolerated non-muslims required tax (jizya) – many conversions • Arab military aristocracy favored – Luxurious lifestyle, relaxed attitude re: Morality Rebellion in 750 brought its end • Persian statecraft techniques – Governors, bureaucratic ministries – vizier, emir – Diplomacy with the West (Charlemagne) • Didn’t work to conquer new territories – Local divisions led to rebellion – smaller Caliphate What factors enabled the rapid spread of Islam in the years after Muhammad's death? Interpretation of the jihad “Struggle” Internal conflict (spiritual and/or moral) missionary work, physical conflict Unifying the Umma & creating the Dar Al-Islam How? •Quran: recitations of Muhammad's visions (Arabic only) •Hadith: Muhammad's sayings •Sharia interpretations of the Quran to establish laws regarding: Marriage, Business, Inheritance, Slavery, Crime Who? •No organized priestly class – Ulama (Muslim theologians) – Qadis (Muslim jurists) – Sufis (Mystics) – missionary work (Persia, India) Abbasid after 1050 • Seljuk (Saljuq) Invaders • Abbasid united with Seljuks to resist internal rebellion and resistance from provincial governors • Caliphs retained nominal sovereign status • Seljuk Sultan became true political ruler • Mongol invasions 1258 ended Abbasid Caliphate Mongol empire Islamic Culture & Society The Awakening • • • • • Role of hajj (movement & diffusion) Muhammad’s example- merchant Geographical position of Muslim World Introduction of Paper – Books No seeming contradiction between faith and Knowledge • Arabic language – unifying force • Renaissance beginnings! Scientific Achievements Sought out scientific understanding • Hindu Numerals – Algebra, Trigonometry • Greek Philosophers (Aristotle, Plato) • Spirit of Inquiry – Scientific process • Medicine – Hospitals, concept of Germs, Anatomy, cataract surgery (modern camera) Urban Nature of Islamic Society Artistic and Architectural evidence Key Cities • Baghdad – Rival of Athens or Rome – Jewel of the World – House of Wisdom, Academies, Libraries – Christians, Muslims, Jews • Cordoba, Spain – Rivaled Baghdad – Street lights, paved roads, hospitals, libraries, palaces, running water – Mosque at Cordoba – Only Christian World Contact Mosque at Cordoba 8th Century Origins of Patriarchy? • Gerda Lerner • Disputes biological determinism • Urbanization breeds patriarchy – Elise Boulding – Hunter gather societies were more egalitarian What was life like for Women in Pre-Islamic Arab Society? The Role of Women According to the Quran … • Rights & obligations for both in marriage • Equal access to salvation • Dowries (free gift) • Child bearing crucial • Wives share property • Obedience to husband • Punishments for indecency • Provisions for wife in case of divorce or death of husband • Polygamy (sake of protection) In Practice… • Foundations of Patriarchal society • Sharia reinforced male dominance & inheritance • Required legitimacy of heritance- guardians, chaperones • Influence of Persia & Byzantine culture – Veiling to ensure modesty – Upper class women’s movement restricted Conclusions: • “… It is also relevant to emphasize that although Islamic laws marked a distinct decline, a Greek, a Roman, and a Christian period had already brought about major losses in women’s rights and status. In effect, Islam merely continued a restrictive trend already established by the successive conquerors of Egypt and the eastern Mediterranean…” –Leila Ahmed, Women and Gender in Islam