* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Solar System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
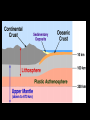
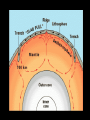
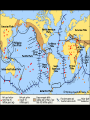
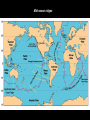
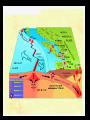
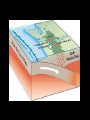
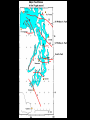
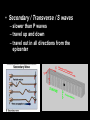
“Our” Earth Plate Tectonics • Tectonic plates – large pieces of the crust and part of the mantle called the lithosphere • seven very large ones and lots of small ones • constantly moving/floating (116cm/year) on the plastic part of the mantle because of convection currents in the soft rock underneath them –this is called continental drift Plate Boundaries • Divergent boundaries – plates move apart – Mid-ocean ridges are mountains created by the rising lava • Divergent Boundary Mid-ocean ridges • Convergent boundaries – plates come together – can develop chains of volcanoes, mountains, and earthquakes • Continental Drift - Tetrionic Plates – subduction is where the denser plate dives under another • Juan de Fuca plate is diving under the North American plate (this is not good) • Animation of Earthquake and Tsunami in Sumatra • Stuck in tsunami For most recent EQ -- http://www.pnsn.org/recenteqs/latest.htm Earthquakes • energy is released as plates slip along a fault line • the focus is where the slippage occurs • the epicenter is the point on the surface above the focus • measured using the Richter Scale • each number increased on the scale is about 10 times the amount of ground shaking and 30 times more energy - the building can withstand winds and typhoons of up to 200km/h (with the top swaying by a maximum of 75cm/0.3inches) and earthquakes of up to 7 on the Richter scale; Built to withstand 200 mph winds and an earthquake of up to 9.5 magnitude. Earthquake Waves • Primary / Longitudinal / P waves – fastest waves – travel out in all directions from the epicenter – compress the earth’s crust • Secondary / Transverse / S waves – slower than P waves – travel up and down – travel out in all directions from the epicenter • Surface waves: – move only across the earth’s surface – causes the most damage because of a circular motion caused by up and down AND back and forth motion Weathering and Erosion - breaking rocks apart • Physical (mechanical) weathering – glaciers moving, water (ice) expanding, wind, and plant roots – erosion: wind and water can loosen and move sediment – deposition: the sediment then builds up somewhere else • Chemical weathering – O, H2O, and CO2 chemically react with many minerals forming new compounds