* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes - Endosymbiotic Theory
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
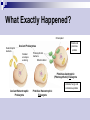
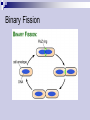
Endosymbiotic Theory The Endosymbiotic Theory Review: What is a theory? What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? The endosymbiotic theory is the idea that a long time ago, prokaryotic cells engulfed other prokaryotic cells by endocytosis. This resulted in the first eukaryotic cells. First proposed by Lynn Margulis Explains the origin of eukaryotic cells Explains the origin of certain membrane-bound organelles What Exactly Happened? Chloroplast Heterotrophic bacteria Ancient Prokaryotes Nuclear envelope evolving Plants and plant-like protists Photosynthetic bacteria Mitochondrion Primitive Autotrophic (Photosynthetic) Eukaryote Animals, fungi, and animal-like protists Ancient Heterotrophic Prokaryote Primitive Heterotrophic Eukaryote Membrane-Bound Organelles Mitochondria (Animals) membranebound organelle that produces energy for the cell Chloroplast (Plants) membrane-bound organelle that captures sunlight and uses it to make food for the cell Evidence in support of the endosymbiotic theory: Similarities between mitochondria, chloroplasts, & prokaryotes: Circular DNA 2. Ribosomes 3. Binary fission 1. Binary Fission