* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Origin of Life
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
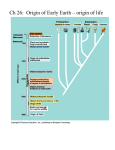
Primordial Earth Theories on the Origin of Life Early Earth and Evolution A THEORY of the origins of the universe Big Bang When? -Approx. 13.5 Billion years ago expansion from singularity -MASSIVE AMOUNTS OF ENERGY! -Energy eventually converted to fundamental building blocks of matter. Evidence? -Expanding universe -Background radiation -Abundance of Hydrogen After Big Bang……. • Stars! – Need hydrogen gas fusion – Form heavier elements – Really big stars go out with a bang supernova! • Planets! – Leftover “mess” from supernova start to accrete into larger objects. (NEWTONS LAW!) – Typically these objects will orbit around a star • SOLAR SYSTEMS! LIFE!!!! • Spontaneous Generation. – Theory (hypothesis actually) that life can randomly emerge from non-living thing • Biogenesis – Theory that life only comes from pre-existing life. • Common Ancestor – Theory that every living organism on the planet is a descendent of an original cell • Question : Where did first life come from??? Oparin-Haldane Hypothesis • All the elements were already present on Earth. • Early atmosphere contained mostly ammonia NH3, hydrogen gas H2, water H2O, and methane CH4. • High temperatures might cause gases to form simple organic compounds. “Prebiotic Soup” • As Earth cooled simple organic compounds collected in the lakes and seas. • Energy from lightning and UV radiation caused chemical reactions to build macromolecules. Key Experiments • Francisco Redi’s Flies – – Where do maggots come from – Bottom Line: no spontaneous generation Key Experiments • Spallanzani – – Bacteria in broth come from air? Or other microbes? – Bottom Line: no spontaneous generation Key Experiments • Louis Pasteur – – Bacteria in broth come from air? Or other microbes? – Key difference from spallanzani? – Bottom Line: no spontaneous generation 1953: Miller- Urey • Stanley Miller and Harold Urey set up an apparatus to simulate the proposed primordial Earth conditions. 1953: Miller- Urey • Stanley Miller and Harold Urey set up an apparatus to simulate the proposed primordial Earth conditions. • Found organic compounds. Debatable points: • Atmosphere probably contained CO, CO2, and N2 • Presence of O2, and CO2 interfere with production of organic compounds. –Organic compounds produced in undersea volcanoes. • Organic compounds came from outer space. Pre-Cell Structures • Organic molecules aggregate spontaneously. • Microsphere: Protein membrane structure • Coacervates: Droplets of lipids amino acids, and sugars. Microspheres Coacervates First Cells: Prokaryotic • Environment: Little or no oxygen Cells were anaerobic. • Environment: Organic food molecules Cells were heterotrophs. • Oldest fossils look like prokaryotes. Cells were prokaryotes. Archaea • Present day cells, thought to be similar to earliest cells. • Unicellular organisms that thrive in harsh environmental conditions. –Anaerobic metabolism. –Inorganic energy sources. Endosymbiotic Theory Creating the first eukaryotes: • Large prokaryotes engulfed smaller prokaryotes. • Mutually beneficial relationship: small cells are protected and large cell gets energy. • Small aerobic cells evolved into mitochondria • Small photosynthetic cells evolve into chloroplast. • Mitochondria and chloroplast have their own DNA. • DNA is circular, like prokaryotes. • Replicate independently of cell. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dSjg_uYS_QY&feature=related Summary 1. Small organic molecules were synthesized. 2. Small organic molecules (monomers) joined to form polymers, like protein and nucleic acids. 3. Molecules could self-replicate. 4. Molecules were packaged into membrane structures- resembling the first prokaryotic cell.