* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution of HSV-1 and VZV.
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative comparative linguistics wikipedia , lookup
Viral phylodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Maximum parsimony (phylogenetics) wikipedia , lookup
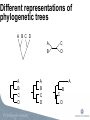
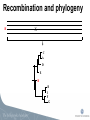
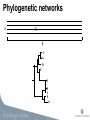
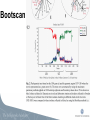
Viral Evolution and Recombination Peter Norberg [email protected] Phylogenetic analysis • Reconstruction of evolutionary history • Relationship • Distance • Common ancestors Tree of Life Viruses and Viral Evolution • Viruses are not living organisms! • but evolving… • Genetic material (DNA or RNA) • Need to adapt to their environment! Different representations of phylogenetic trees A B C D A B A B C D A B C D C D A B C D Bootstrap -A way to get “statistical significance” of a certain topology -Construct several new sequence sets (1000 st.) -A new sequence set is generated by randomly picking of columns from the original set -Apply the phylogenetic algorithm on all sets. -Make one consensus tree from all trees Bootstrapping A: AACTTAACCACGCTATCGATGCAATTATATA B: AATTTGACTGCGGTACCGATCCAATTATATA C: AATTTGACTGGGCTACCGATCCAATTATATA D: AACTTAACCGCGCTACTGATCGAATTATATA A: CACC B: TGCT C: TGCT D: CAGC A A 1 96 A 3 D C B B B C 1 96 C 3 D D Recombination • A powerful genetic mechanism • Used by all animals (extremely few exceptions) • Beneficial despite “the cost of sex” • Speeds up evolution (up to 10,000 times) • Accumulate beneficial mutations • Expel deleterious mutations • Bacteria through HGT •Viruses! Recombination Recombination and phylogeny X H C A C A D D E E H B I F G H B I F G Recombination and phylogeny H X C A D E H B I F G Phylogenetic networks H X C A D E H B I F G Methods for detection of recombinants -Detecting conflicting phylogenetic signals • Phylogenetic networks (SplitsTree) • Can be due to recombination or homoplasy Phylogenetic network Methods for detection of recombinants -Analyze conflicting phylogenetic signals, recombination vs homoplasy, and define breakpoints •Bootscan (SimPlot) •Similarity plots (SimPlot) •Statistical tests (phi-test) •RDP, Geneconv, MaxChi, Chimaera, SisScan, 3Sec, LARD, Topal, …. (RDP) Bootscan