* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4-Amenorrhea [Dr.Mandeel]. - King Saud University Medical Student
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Sexually dimorphic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Gynecomastia wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal breast enhancement wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Polycystic ovary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Androgen insensitivity syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
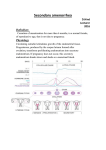
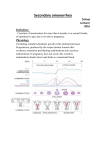
Dr. Hazem Al-Mandeel, M.D Assistant Professor & Consultant Obstetrics & Gynecology College of Medicine King Saud University OB/GYN Rotation-course 481 GYN 1ry Amenorrhea: is the lack of onset of menses by age 16 in female with 2ry sexual characteristics OR by age of 14 in female without 2ry sexual development 2ry Amenorrhea: is the cessation of menses for a period of 6 months in a female who previously had initiation of menses • Gonadal Failure • Congenital Absence of the vagina • Constitutional delay 43% 14% 10% • Chronic anovulation 39% • Hypothyroidisim/Hyperprolactinemia 20% • Weight loss/anorexia 16% UterusAbsent 5 -Reductase def. 17-20 Desmolase def. 17 Hydroxylase Def. (All XY Karyotype) Primary Sexual characteristics HCG + Absent Present PE HCG -ve Pregnancy No Primary Karyotype •XX •Y line •Turner (XO) Normal High FSH Normal •Kallman’s Syndrome •Physiologic Delay Yes Secondary R/O Asherman’s Cx Stenosis PE Normal TSH, PRL, FSH Mullerian Abn AIS True Hemaphrodite TSH, PRL, FSH TSH Abnormal Prolactin High FSH High HypoThyroidism HyperThyroidism Normal Normal Normal Normal Low Estrogen PCOS Idiopathic Ovarian Neoplasms Obesity Cushing’s CAH CNS Exam Chronic Disease Hyperprolactenemia •Ovarian Failure •Radiation •Chemo •Infection •Autoimune •Galacrosemia •Idiopathic Pituitary Hypothalamic Lesions: Tumors Infection Infarction Failure Toxic 1-TURNER SYNDROME: 45XO 2-Mosaicism of Turner’s: XO/XX not always short, they will have menses , get pregnant then develop premature menopause 3-Structural abnormalities of the X chromosome: deletion of the short arm of the X chromosome Short stature deletion of the long arm normal Ht., 2ry Amenorrhea, & streak gonads 1ry amenorrhea No breast development Normal ♀ genital organs (external /internal) Streak gonads (ovaries are replaced by nonfunctioning tissue) Short stature Webbed neck (Short broad neck) with a low hair line Cubitus vulgus Shield chest / Widely spaced nipples High arched palate Short 4th metacarpal Coarctation of the aorta or VSD Horse shoe kidney or single kidney Lymphedema 4-Pure gonadal dysgenesis : 46XX, mutation in an autosomal gene accelerated germ cell loss streak gonads. Features: ♀ genetalia with normal mullerian structures 5- Pure gonadal dysgenesis : 46 XY. Features: normal♀ genitalia and mullerian structures with streak gonads ↑ risk of malignancy 6- 17-α hydroxylase deficiency (rare) ovarian synthesis of estrogens 1ry Amen Sexual immaturity cortisol ↑ ACTH ↑ Na K ↑ BP ↑ Progestrone as it is not converted to cortisol 7- Galactosaemia (rare) galactosaemia is toxic to oocytes Anosmia & Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism X linked ----Mutation in the KAL gene More common in ♂ > ♀ Midline defects Cleft lip & Palate Somatic defects color blindness, renal agenesis, retinitis pigmentosa, neurosensory deafness Lack 2ry sexual chct & the ability to smell HT & bone age appropriate for age CNS tumors GnRH pulses LH & FSH estradiol Hypothalamic Lesions Craniopharyngioma granuloma, aqueduct stenosis , & encephalitis CNS tumors interfere with the –ve feedback of Dopamine on Prolactin ↑ Prolactin Other causes of HypoGonadotropic Amen hypothyroidism Functional GnRH deficiency May present with or without Breast development Physical stress delay menarche Each year of athelitic training before menarche delayed menarche 5 M Osteoporosis could occur with prolonged periods of Amenorrhea, low body Wt 1. HYPOTHALAMIC CAUSES: CNS lesions (tumors) Stress, Excessive exercise & low body Wt 2. PITUITARY CAUSES: Hyperprolactinemia Hypothyroidism ↑ TRH ↑ prolactin 3. OVARIAN CAUSES: Polycystic ovarian disease/syndrome 4. OUTFLOW TRACT OBSTRUCTION: Imperforate hymen Transverse vaginal septum XY Karotype produce MIF Mullerian structures are absent Complete/ Partial absence of androgen receptors X-linked recessive or dominant Female external genitalia with Short blind vagina Testosterone normal ♂ range Breast development due to peripheral conversion of androgens to estrogens Sexual hair is absent due to absence of androgen receptors Gonadectomy after puberty ↑ risk of malignancy (gonadoblastoma, dysgerminoma) Autosomal recessive Formation of the ♂ external genitalia requires 5α REDUCTASE testosterone dihydrotestosterone Formation of the internal wolfiane structures respond directly to testosterone External genitalia ♀ with mild musculinization Absent uterus At puberty testosterone secretion virilization Etiology ? Failure of mullerian duct development absence of the upper vagina, cx & uterus (uterine reminants may be found) The ovaries & fallopian tubes are present Normal 46XX ♀ with normal exrenal genitalia Pt present with 1ry amenorroea 47% have asociared urinary tract anomalies 12% skeletal anomalies Rx psychological counseling surgical treatments: vaginoplasty, excision of utrine reminant (if it has fuctioning endometrium) The least common presentation of 1ry Amenorrhea All patients are 46 XY Testosterone or N FSH/LH ↑ A. 17-20 DESMOLASE DEFICIENCY The enzyme required for the synthesis of Androgens androgens estrogen The testes produce MIF therefore no mullerian structures ♀ external genitalia Insufficient estrogens for breast development B. 17 α HYDROXYLASE DEFICIENCY Similar to 17-20 desmolase deficiency. Cortisol synthesis also ↑ BP, hypernatraemia & hypokalaemia C. AGONADISM Degeneration of the testes (in utero) after the production of the MIF WHAT IS 2RY AMENORRHEA? Cessation of menses for a period of 6 months or 3 consecutive menstrual cycles in a ♀ who previously had initiation of menses WHAT IS THE PREVELANCE OF AMENORRHEA? 1.8-3% WHAT IS THE CLASSIFICATON OF 2RY AMENORRHEA? Hypergonadotropic Hypogonadotrpic Euogonadotrpic Hperprolactinemia Anatomic defects Stress ↑ β-endorphins GnRH FSH LH Estrogens Exercise Excessive streneous exercise e.g.: runners Mechanism Similar to stress Wt. loss “Anorexia nervosa” More frequent in adolescent & young adults 0.5-1% of women aged 15 –30 years 15% < Ideal Body Wt. Functional “Non of the above causes” No LH pulses or persistent pulse frequency of “Luteal Phase ” 2ry to neurotransmitter abnormality of the CNS (? ↑ Opioid activity) IS IT OF ANY CONCERN IF THESE YOUNG WOMEN BECOME AMENORRHEIC ? HYPOESTROGENISM is the main concern WHY IS IT MORE WORRYING THAN THE MENOPAUSAL WOMEN ? During adolescence estrogen plays a critical role in determining PEAK BONE DENSITY which reached in the 2nd decade of life IS THERE ANY EVIDENCE OF ITS EFFECT ON THE BONES? Amenorrheic Athletes Bone Mineral Density (BMD) in lumbar spines, femur, tibia Athletes with menstrual irregularities BMD but less than athletes with regular cycles Anorexia nervosa Pt BMD (0.64) Anorexia nervosa Pt may have osteoporotic fractures SHEHAN’S SYNDROME Pituitary failure following sever post partum hemorrhage Deficiency of all pituitary hormones FSH & LH Failure of ovarian follicular development estrogen Amenorrhea Rx HRT In training intensity to a level where regular menses resume HRT Cyclic estrogen / progestrone; e.g.: Premarin continuously + Medroxyprogestrone acetate for 12 days OCP better compliance Anorexia nervosa Psychiatric Rx + HRT Long term follow up Frequent relapses after attaining ideal body wt. Functional Amennorhea HRT / ovulation induction Polycystic Ovarian Disease / Syndrome Amenorrhea / anovulatory cycles Enlarged polycystic ovaries Infertility Hyperinsulinemia / Obesity Hyperandrogenism / hirsutism ↑ LH Acyclic estrogen production / unopposed by progesrtrone ↑ risk of endometrial hyperplasia/Ca Inheritable disorder with a complex inheritance pattern WHAT IS PREMATURE OVARIAN FAILURE (POF) ? 2ry Amenorrhea ↑ FSH & LH Estrogen Before the age of 40 years WHAT IS THE INCIDENCE OF POF ? 1% WHAT IS THE CAUSE? Unknown / autoimmune / genetic factors Associated autoimmune disease 39% WHAT ARE THE PATHOLOGICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF POF ? Ovarian sclerosis & lack of follicles Resistant ovary syndrome HOW TO MANAGE POF? R/O other autoimmune diseases RH factor ANA, Antithyroid Antibodies, Antichromosomal Antibodies, glucose, cortisol, Ca , Ph, TSH HRT to prevent osteoprosis Spontaneous pregnancy can occur in 8% of women with POF on HRT The most common pituitary cause of 2ry Amenorrhea Causes -Pituitary adenoma -Idiopathic -Loss of inhibition by dopamine Hypothalamic or pituitary stalk lesions -Hypothyroidism -PCOS -Medications phenothiazines , haloperidol monoamineoxidase inhibitors, TCA, H2 receptors blockers Galactorrhea 1/3 of Pt Amenorrhea/ Hyperprolactinemia Pt at risk of osteoporosis due to estrogen TREATMENT - Hypothyroidism L-Thyroxin If still amenorrheic after RX Parlodel + Thuroxin -If no substitute for the medications that cause hyperprolactinemia HRT -Hypothalamic or pituitary stalk lesions Surgical excision PITUITARY ADENOMA (PROLACTINOMA) *Macroadenoma > 10 mm Respond to medical Rx Dopamine agonist (bromocriptin) size of the tumor & prolactin level Pt not responding to medical Rx or not tolerating it Surgery/ Irradiation *Microadenoma < 10mm remain stable in size Rx Bromocriptin prolactin level to normalize the menstrual cycle IDIOPATHIC HYPERPROLACTINEMIA Rx Dopamine agonist Bromocriptin or Pergolide Side effects of dopamine agonists -Postural hypotension -Nausea -Headache -Nasal stuffiness Starting with a low dose & gradually ↑ it helps to avoid the side effects Uncommon cause of 2ry Amenorrhea Asherman’s Syndrome Hx of D/C for RPOC after abortion / puerperium or previous uterine infection Intrauterine Adhesions Normal hormones Negative progestrone chalange test Dx HSG / HYSTROSCOPY Rx Hystroscopic resection of the adhesions followed by estrogen therapy