* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download IB Business & Management Unit 4.2 Marketing Planning
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Food marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
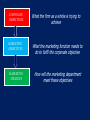
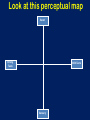
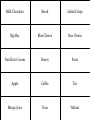
IB Business and Management 4.2 Marketing Planning (Including introduction to the four P’s) Learning Outcomes • • • • • • • • • • To understand the elements of a marketing plan (A01) and the role of market planning (A02) To understand (A02) and apply the 4P’s of the marketing mix to given situations (A04) Discuss the effectiveness of a selected marketing mix in achieving marketing objectives (A03) To understand the difference between target markets and market segments in a given situation (A02) Discuss possible target markets and market segments in a given situation (A04) To understand the difference between niche market and mass market (A02) How organisations target and segment their market and create consumer profiles (A02) To create (A02) and analyse a product position/perception map (A04) The importance of having a unique selling point (USP) (A02) How organisations can differentiate themselves and their products from their competitors (A03) Essential Discussion Questions To what extent is developing a successful marketing plan scientific? Do you think it is a case of using appropriate tools that will inform you of the best approach or is it more subjective and ‘hunch’ based? To what extent do you think a clear, well researched marketing plan guarantees success? MARKETING PLANNING The Role of Market Planning “The process of formulating marketing objectives and devising appropriate marketing strategies to meet these objectives” THE PLANNING PROCESS: 1. Marketing Audit – Where are we now? 2. Marketing objectives – Where do we want to be? 3. Marketing strategies – How will we get there? 4. Monitoring & review – Are we on track? 5. Evaluation – Did we succeed? Marketing Objectives Marketing objectives should not be set in isolation They should be compatible with the firm’s Corporate Objectives Often set by directors of the company They will also need to consult other business functions (finance and production for example) CORPORATE OBJECTIVES What the firm as a whole is trying to achieve MARKETING OBJECTIVES What the marketing function needs to do to fulfil the corporate objective MARKETING STRATEGY How will the marketing department meet these objectives Types of Marketing Objectives • • • • • • • Increasing sales (By volume, By value) Increasing market share To enhance the brand image To reposition the brands image Raising brand awareness Increasing brand loyalty Improving corporate image Setting Marketing Objectives Marketing Objectives must be SMART S mart M easurable A greed R ealistic T imed E.g. To increase market share by 5% in the next 2 years Marketing Strategy Marketing Strategy is the plan for how the Marketing Objectives are going to be achieved What marketing strategies might be used to help achieve the following types of objectives? • Increasing sales (By volume, By value) • Increasing market share • To enhance the brand image • To reposition the brands image • Raising brand awareness • Increasing brand loyalty • Improving corporate image How might a business’ marketing mix differ when trying to implement these strategies? Reasons why marketing objectives are not achieved Internal Constraints • • • Financial Personnel Unrealistic objectives External Constraints • • • Competition The economy Tastes and fashions Benefits & Limitations of Market Planning BENEFITS Helps identify potential problems and how to solve them SMART objectives will improve chance of success LIMITATIONS Plans can become outdated if not quick enough to react to market conditions The process consumes valuable resources: Time, Capital, Expertise A clear plan shared across business Unclear objectives could lead to an functions improves coordination ineffective and unclear marketing plan Helps plan appropriate budget to maximise use of resources A clear plan and direction could improve employee motivation and inspire confidence So…How to make a Marketing Plan Successful? • Must be reflective process • Continually reviewed and evaluated • Should be flexible and adaptable according to changing external factors and market conditions THE MARKETING MIX (THE FOUR P’S) The Marketing Mix? “The key elements of a marketing strategy that ensure the successful marketing of a product” The Marketing Mix- Product A product can be a good or a service It must meet the wants or needs of customers Product design decisions can include: • Function • Features • Design • Quality • Branding The Marketing Mix- Price Pricing is one of the hardest decisions in the marketing mix. Why? • What if the product is overpriced? • What if the product is underpriced? What information might businesses need to know when setting their prices? Pricing Decisions depend on: • • • • • • Demand and Supply Consumer perceptions Business objectives Competition Costs of production. Corporate image The Marketing Mix- Place Place is about making the product available to customers in the right place and at the right time. Place decisions: • Distribution channels • Opening times • Location • Logistics The Marketing Mix - Promotion • Promotion is all of the activities involved in informing customers about a product and in persuading them to buy it • What could this involve? An Appropriate Marketing Mix Will: • Ensure consumers needs and wants are met • “Right product, at the right price, available at the right place and communicated through the right promotion channels (media)” Do the companies we have chosen have an appropriate marketing mix? Ongoing Task – In pairs develop an Appropriate Marketing Mix for… • • • • • • • A new water A new cereal A new sports drink A new airline A new school A new chocolate bar A new…..? Mr. Owen’s CAS group – perhaps you could develop appropriate marketing mix for your project? TARGET MARKETS & MARKET SEGMENTATION Market Segmentation • Most businesses can’t sell their products to everyone • Instead they break the market down into smaller pieces and then try and sell to these smaller groups • The smaller groups are called market segments • They consist of customers who buy similar products • These consumers are known as the target market for a product Definition “The process of splitting a market into distinct groups of buyers to better meet their needs. It is normally based on demographic, geographic and/or psychographic factors” Demographic Factors • Demography is the study of the characteristics of the human population. Demographic variables include: • Age • Gender • Race and Ethnicity • Marital status • Religion • Language • Income and Socioeconomic class Socio-Economic Groupings Group Description A Higher managerial, administrative or professional e.g. surgeon or company director B Intermediate managerial, administrative or professional e.g. teachers, solicitors C1 Skilled non-manual e.g. sales assistants, shop floor supervisors C2 Skilled manual e.g. electrician, plumber D Semi skilled e.g. assembly line workers, cleaners E Unskilled, pensioners and unemployed Marketing terms • Marketers have come up with many ACRONYMs for various demographic groupings. • An example is DINKY – Double Income No Kids • Here are some more….. Can you guess what they are and think of what types of products that would be targeted at them? NILK No Income Lots of Kids GLAM Greying Leisured, Affluent, Middle Aged OINK One Income, No Kids YUPPIE Young Urban Professional GUPPIE Green Yuppie YAPPIES Young Affluent Parents SITCOM Single Income, two children, outrageous mortgage RAPPIES Retired Affluent People SINDI Single, Independent, Divorced SINBAD Single Income, No Boyfriend And Desperate Tweenagers 7-12 year olds Kidults Adults who buy kids products Geographic Factors • Geographic factors can have a huge influence on demographic factors such as race, religion, language. Geographical factors include: • Location • Climate Psychographic factors • • • • • Emotions and Lifestyle Values Status Culture Hobbies and Interests Developing a Consumer Profile • The demographic/ psychographic details of the average user of a product • Businesses use this knowledge to help them to identify customers needs and identify new segments to target For Example…What could be the different Consumer Profiles for Shampoo? Task • Look at the products on the following slides and see if you can identify who the target market is • What do you think their Consumer profile would be? How Customers Differ • Market segmentation is needed because customers are not all the same! They differ in their needs and wants. • For example, customers differ in the… – Benefits they want from a product – Amount they are able to or willing to pay – The media they see – Quantities they buy – Time and place that they buy Example – Kelloggs: By providing a range of products Kellogg's can meet a wide variety of different customer needs and wants and potentially appeal to the whole market! SALES MARKET SHARE LOYALTY / REPUTATION PROFITS ECONOMIES OF SCALE Example - McDonalds Example - Saga Saga is a company that offers many different products…. All aimed at people aged over 50 Benefits of Segmentation • Businesses are successful when they provide things that customers want • Segmentation allows businesses to develop products that more closely meet customer needs • A range of products can be made to appeal to different market segments • Also allows promotional spending to be targeted more effectively – E.g. adverts not put in the wrong kind of newspaper or magazine – Sales promotions (e.g. price discounts) not offered to customers who don’t respond to them Difference Between A Niche and Mass Market Strategy Niche Market: “ A narrow, smaller or more specific market segment within a larger market” Mass Market: “A large or broad market that ignores specific market segments” Reflection Time • In Pairs can you discuss the benefits and limitations of a Mass approach verses a Niche approach. • Suggestions on a post it and placed in the appropriate column on the board. MARKET POSITIONING Look at this perceptual map Sweet Strong Taste Mild Taste Savoury Task • Copy the market map from the previous slide onto a piece of paper. • Look at the different foods on the next slide and see if you can put them in the correct place on the axis according to whether they are sweet or savoury and whether they are mild or strong tasting Milk Chocolate Bread Salted Crisps Big Mac Blue Cheese Raw Onion Vanilla Ice Cream Honey Pasta Apple Coffee Tea Mango Juice Tuna Walnut How does this relate to business??? Perception maps can be used by businesses to analyse competition within an industry • This is known as market mapping or perceptual mapping • It is used to help with market positioning What is a market map A market map is a tool used by businesses when they are considering entering a new market or launching a new product • A market map allows the business to examine the existing competitors/products in a market • They can see which areas of the market are overcrowded or spot potential gaps • In order to construct a market map the company decides on 2 key factors of the market • Example market map – female clothes retailers High Price Burberry Karen Millen French Connection classic fashion Top Shop New Look H&M Low Price Primark Market Map for Bottled Water High Price Everyday Luxury Low Price Task 1. 2. 3. 4. Copy down the market map from the previous slide. Add onto the map the following competitors: Add on 2 more brands of your choice Why do you think it would be hard for a product to succeed in the ‘high price’ and ‘everyday’ quadrant? 5. If a new bottled water was to enter the market where do you recommend they try to position themselves? 6. How would you recommend that a new bottled water tried to ‘differentiate’ it’s self from competitors? Choosing the right factors Each market will have different key features. • Examples could be: • High Price/Low Price • Youthful/Older • Modern/Traditional • Masculine/Feminine • Fashion/Classic • Aesthetic/Functional • Luxury/Everyday Question What factors do you think could be used in a market map for the following markets? 1. Female clothes retailers 2. Takeaways 3. Cars Task • As a class we are going to construct a market map of restaurants. • 1. Brainstorm a list of restaurants in your local area • 2. Copy the axis on the next slide into your notes • 3. Position the competitors on the map Market Map for Restaurants High Price Special Occasion Everyday Low Price What could these pictures be referring to? Unique Selling Point (U.S.P.) “A product’s feature(s) that differentiate it from other competing products” • • • • Importance of having a USP: Creates a competitive advantage Can attract more customers higher sales Promotes customer loyalty increased sales Can create barriers to entry to deter potential competitors Developing a USP Businesses can use the marketing mix as a way to create USP’s. For example: • • • • Product – features, quality, design, (Apple products) Price – Low to undercut or high for superior product Place – distribution channels, locations, outlets Promotion – slogans, advertising, sponsorship, endorsements, brand image, Task 5 mins – In pairs • In your pairs you need to research and provide at least one example of how a business has developed a USP using your assigned element of the marketing mix (the 4 P’s) • Feedback your findings but also consider: – Has it worked? – Why did the business choose to differentiate in this way? – Do you think it could be better – how and why? Company Case Study Time (A03) For your business, analyse how they differentiate themselves and their products from competitors? 5-10 Mins and feedback your thoughts to the class – maybe add to our wall display? Is it the best strategy in your opinion?













































































![AnIntroductiontoMarketing[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008555155_1-1af3b70cfa03f8a4f7957dd38251412b-150x150.png)








