* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
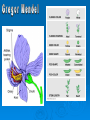
• July 20, 1822 - January 6, 1884 • Known as the “Father of Modern Genetics” • Austrian monk and scientist that worked with pea plants to discover law of inheritance. • saw that characteristics are passed from parent to offspring • work not recognized by scientists until the early 20th century • Mendel used pea plants because they reproduce sexually and contain sex cells called gametes. Gametes of peas are in the same flower and fertilize, unite male and female gametes, through pollination. (Self-pollinating) • Mendel was careful with research. Studied only ONE train at a time and used cross pollination (took male gametes from one flower and united them with female gametes of a different flower). • heredity = the passing on of characteristics from parents to offspring • traits = characteristics that are inherited • Genetics = branch of biology that studies heredity • gene = the functional unit of heredity (also called a locus) ; passed from parent to offspring • Organisms have two factors that control each trait. 1. Characteristics determined by factors passed down from parents to offspring - Genes passed down and located on chromosomes - Called alleles, different forms of a gene - Located on different parts of chromosomes 2. Principle of Dominance * States that some alleles will be dominant and some will be recessive - dominant = observed trait (shown as uppercase letter) ex. Tall = T - Recessive = trait that is masked or disappears (shown as lowercase letter) ex. Short = t • only shown when dominant allele not present * Two different organisms can look alike but have different gene combinations • phenotypes = the way an organism looks and behaves; the physical appearance • genotype = the genetic combination of the organism Phenotype = brown hair Genotype = BB or Bb Homozygous = same alleles for a trait (purebreed) Ex. TT, tt, BB, bb, AA, aa Heterozygous = different alleles for a trait Ex. Tt, Bb, Aa * Heterozygous individuals can also be called hybrids, offspring of parents that have different forms of a trait 1. Law of Segregation * States that during gamete formation, each allelic pair will segregate (separate) from each other leaving each gamete with one allele for each gene or trait. 2. Law of Independent Assortment * States that genes for different traits can segregate independently during gamete formation and pair at random. Rules for combining probabilities 1. Probability that one event out of a set of mutually exclusive events will occur is the sum of their probabilities. (Mutually exclusive events cannot occur together.) (Look for the word “or”.) Ex. What is the probability of rolling a 3 or a 6 on a 6-sided dice? p = 1/6 + 1/6 = 2/6 or 1/3 2. Probability that both of two independent events will occur is the product of the independent probabilities of the single events. (Independent events do not affect each other.)(Look for the word “and”.) Ex. What is the probability that I roll a 1 and a 3 when rolling two 6-sided dice? p = 1/6 x 1/6 = 1/36