* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download advances in genetics
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Gene prediction wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene Disease Database wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
History of biotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Biotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering in science fiction wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
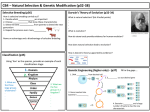
ADVANCES IN GENETICS Sequencing DNA • Before we can produce organism’s with desired traits, we must first sequence DNA. • What do we call the process of sequencing DNA? – DNA Fingerprinting DNA Fingerprinting • Application of knowledge: From your readings, how is DNA fingerprinting used in today’s world? Advances in Genetics • As humans, we are capable of producing organisms with certain desirable traits? • Identify the methods that allow us to do this: – Selective Breeding – Genetic Engineering – Cloning What is selective breeding? • The human practice of breeding animals or plants that have certain desired traits. • What are some examples of selective breeding from our articles? Selective Breeding Interesting Fact! • Is that a fact!? As a result of selective breeding, the smallest horse if the Falabella, which is only about 76cm tall. The largest is the Shire, originally bred in England. The Shire can grow to mare than 1.73m high at the shoulder and weigh as much as 910kg. What is SELECTED BREEDING? • Breeding: males and females mate to produce offspring • Selective breeding: people choose organisms (males and females) with desired traits to produce offspring with the desired traits Dogs That Changed The World • Watch this video on how selective breeding has changed the Saluki breed throughout history. • Speedy Saluki • Answer this question in your notebook: Why is it important for the Bedouin people to selectively breed Saluki for speed and sight? Dogs That Changed The World • Think, Write, Share • Ask yourself: Are there any “cons” to selectively breeding dogs for certain traits? • Write your answer on your paper • Share and discuss your answer with your table. Watch this video: Hard-Wired • Discuss any changes you would make to your previous answer after watching this video. What is SELECTED BREEDING? • Farmers SELECT and save the BEST corn seeds. • The seeds are planted the next year to grow better tasting corn. Selective Breeding • Imagine this: You are a farmer. You support your family financially by growing corn. Your neighbor also grows corn, so you must compete with him to have the best corn in town! • How can you use selective breeding to increase your profits in future years? Selective Breeding • Another type of selective breeding is called Hybridization. • Hybridization: the controlled breeding of organisms with different genes in order to produce offspring with both desired traits. Selective BreedingHybridization • Schnauzer + Poodle = Schnoodle SELECTED BREEDING • HYBRIDIZATION • Two different types of colored corn produce corn with BOTH colors • Corn resistant to insects is crossed with corn that has lots of kernels. SELECTED BREEDING • Inbreeding: organisms (males and females) with SIMILAR genes mate to produce offspring with similar traits • Possible problems: “bad” genes are also passed to the new generation What is Genetic Engineering? • The manipulation of individual genes within organisms. • Also called “gene splicing” because a DNA molecule is cut open, and a gene from another organism is spliced into it. Genetic Engineering • Genes may be even transferred from one organism to another! • What article did you read that discussed this form of genetic engineering? – Green Flourescent Protein! GFP was transferred from jellyfish into many different organisms (fruit flies, mice and rabbits). Genetic Engineering • Use your prior knowledge and your article readings to help you answer this question: • In what ways can we use genetic engineering? Genetic Engineering • Watch these videos on how genetic engineering is an integral part of today’s agricultural processes. • 3rd and 5th: History's Harvest: Genetic Engineering and Agriculture • 4th and 6th: History's Harvest: Genetic Engineering and Controversy Genetic Engineering Interesting Fact • Did you know? Gene therapy is an experimental field of medical research in which defective genes are replaced with healthy genes. • One way to insert healthy genes involves using a delivery system called a “gene gun” to inject microscopic gold bullets coated with genetic material. • Genes and DNA: Genetic Engineering Genetic Engineering A Gene Gun! What is cloning? • Cloning is the process of producing an organism with an EXACT copy of another organism’s DNA. • In what ways was cloning described in the articles you read? What is CLONING? • CLONING: scientists produce an offspring that has the EXACT same DNA as one adult 1. Scientists remove the DNA from an EGG cell 2. Scientist put the DNA from an adult cell into the egg cell 3. Scientists put the EGG into a female animal to grow 4. The offspring is an EXACT COPY of the adult Hello, Dolly! • OL: Watch this video on Dolly, the first mammal ever cloned. • Hello, Dolly: One Controversial Sheep • AC: Watch this video on the process of cloning Dolly the sheep. • Genetics: Cloning GENETIC ENGINEERING • Genes from one organism are transferred into the DNA of another organism. • Also called “gene splicing” because a DNA molecule is cut open, and a gene from another organism is spliced into it. • WHY? Produce medicines, improve food crops, may cure genetic disorders. • Gene therapy – process of inserting working copies of gene into a person’s cell. The person has a genetic disorder. Trace the process of cloning Dolly After watching the video and reading, list the four steps scientists performed in order to clone Dolly the sheep. 1. Scientists remove the nucleus from one of Dolly’s EGG cells 2. Scientists put the nucleus from an adult cell into the egg cell 3. Scientists put the EGG into a female animal to grow 4. The offspring is an EXACT COPY of the adult