* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download From gene to protein 2
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
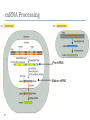
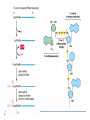
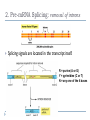
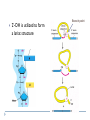
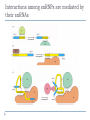
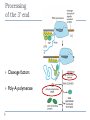
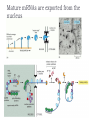
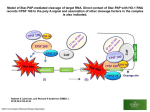
Molecular Biology of the Cell. 2002. Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson, Julian Lewis, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, and Peter Walter. From Gene to RNA Kanokporn Boonsirichai Orientation matters in transcription Figure 7-10 Essential Cell Biology (© Garland Science 2010) Question to consider Could RNA polymerase used for transcription be used as the polymerase (primase) that makes RNA primer required for replication? Why or why not? Molecular Biology of the Cell. 2002. Bruce Alberts, Alexander Johnson, Julian Lewis, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, and Peter Walter. RNA Processing Kanokporn Boonsirichai Gene organization Bacteria Uninterrupted coding sequence Genes are grouped together in an “operon”. promoter gene A gene B gene C Eukaryotes Coding sequence is interrupted by “introns”. Coding sequence is broken into pieces of “exons”. Figure 7-17 Essential Cell Biology (© Garland Science 2010) mRNA Processing Pre-mRNA Mature mRNA Eukaryotic mRNA Processing Capping Splicing Removal of introns 3’cleavage Addition of 7-methylguanosine at the 5’ end Cleavage of the transcript at the 3’end of the gene Polyadenylation Addition of 150-250 adenine ribonucleotides at the 3’ end 1. Addition of 5’ cap 2. Pre-mRNA Splicing: removal of introns Splicing signals are located in the transcript itself. R = purine (A or G) Y = pyrimidine (C or T) N = any one of the 4 bases 2’-OH is utilized to form a lariat structure Branch point Spliceosome A complex of snRNPs (small ribonucleoproteins) Interactions among snRNPs are mediated by their snRNAs How is Fidelity Achieved? snRNAs are associated with snRNPs. Several components of the spliceosome are carried on the phosphorylated tail of RNA polymerase(to keep track of introns and exons). The “exon definition hypothesis” Exon size is somewhat uniform (averaging about 150 nucleotide pairs). Exon-intron boundaries are marked with spliceosome components Other Splicing Systems Transplicing => attachment of two different RNAs What might be the importance of RNA splicing? Alternative splicing allows for the production of multiple related proteins from a single transcript. Processing of the 3’ end Cleavage factors Poly-A polymerase Cleavage signals Poly-A addition Mature mRNAs are exported from the nucleus Questions to consider What do you think might be the reasons for the eukaryotes to have their mRNA processed?