* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gregor Mendel and Basic Genetic Principles
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified organism containment and escape wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
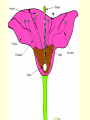
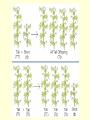
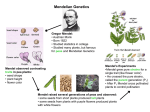
Gregor Mendel & Basic Genetic Principles Who is Gregor Mendel? • Austrian Monk that experimented with pea plants. • He discovered the basic principles of genetics. Pea Plants • Pollination occurs easily within the flower. • Relatively short life cycle (2-3 weeks). • Have 7 characteristics with contrasting forms. Pollination • Movement of pollen between sexual parts of flowers. • Self Pollination – pollination that occurs within one flower. • Cross Pollination – movement of pollen from one flower to another. 7 different traits of pea plants • Seed shape – round/wrinkled • Seed color – yellow/green • Seed coat color – colored/white • Pod shape – inflated/constricted • Pod color – green/yellow • Flower position – axial/terminal • Stem length – long/short Mendel’s 1st Experiment • Mendel created pure–bred pea plants of each characteristic. Ex. Tall/Short, Green seeds/Yellow seeds. • He crossed these plants together (P1 or Parent generation). • Offspring: ALL TALL! (F1 generation). st 1 Mendel’s Law Law of Dominance • When organisms with contrasting traits are crossed, only the Dominant trait appears in the offspring. Mendel’s 2nd Experiment • Mendel took those F1 generation plants and crossed them. • F2 generation results: 3 TALL, 1 SHORT = 3:1 phenotypic ratio. • 1 TT, 2 Tt, 1 tt =1:2:1 genotypic ratio Mendel’s 2nd Law Law of Segregation • Factors occur in pairs and separate during gamete formation only to recombine again during fertilization. Vocabulary • Dominant gene – gene that prevents the expression of another. Ex. Brown hair – represented with a capital B. • Recessive gene – gene that is not expressed, it is usually hidden by a dominant gene. Ex. Blond hair – represented with a lower case b. • Allele – dominant and recessive forms of genes. • Genotype – genetic makeup of an organism regarding its characteristics.(TT, Tt, tt) • Phenotype – physical appearance of an organism. (Tall/Short) • Heterozygous – have 2 different alleles for a particular charateristic. (Ex. Tt = a heterozygous tall plant) • Homozygous – have the same alleles for a particular characteristic. (Ex. TT = a homozygous tall plant & tt = a homozygous short plant) • Hybrid – Common term for heterozygous. Ex. Tt • Monohybrid Cross – Cross between two parents that deals with only one trait. • Dihybrid Cross – Cross between two parents dealing with two different traits. • Incomplete dominance – Blending, when both traits express themselves. • Sex linked traits – Involves genes that are located on the X chromosome. figure 10-13.jpg Figure 10.13 Figure 10.13 Mendel's law of independent assortment of alleles • Alleles of different genes are assorted independently of one another during the formation of gametes. • Mendel determined this law by crossing plants containing two different traits. (Ex. True breed round & yellow seeded plants (RRYY) with true breed wrinkled & green seeds (rryy) figure 10-07.jpg Figure 10.7 Figure 10.7