* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
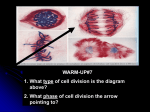
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Notes To be used with Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Guided Notes Before Meiosis lets look back at Mitosis Genes and Heredity • Heredity the passing of traits from parents to offspring. • Genetics the study of heredity (the passing of traits) • Each human cell contains 30 thousand different genes Genes and Heredity Genes: • Factors that control organism traits or characteristics. • Part of a chromosome containing the genetic code • Passed on from parent to offspring. • All of your genes are located on 23 pairs of chromosomes Alleles • Alleles: part of a gene that is located on a chromosome. Example: – Height(gene): – tallness or shortness(alleles) • The alleles determine how each gene is expressed. At least two alleles for one gene. Locus: Location of gene on a chromosome. TT t t Chromosomes Sister Chromatid Chromosome Homologous Chromosome Homologous Chromosomes: -a pair of chromosomes that contain genes for the same traits. -one chromosome is from mom the other from dad. -same size & centromeres are in same location. Amniocentesis • Amniocentesis: a medical procedure used in prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities. • Chromosomes are taken from the amniotic fluid. Karyotype • The chromosomes from the amniotic fluid are then placed on a karyotype. • A karyotype is a chart of an organism’s chromosomes. Karyotype Next, the chromosomes are matched up according to: 1. if they came from mom or dad. 2. how tall they are. 3. centromere location. Karyotype A karyotype can reveal if a person… 1. is, male or female 2. has a normal number of chromosomes 3. has an abnormal number of chromosomes. Example: Down’s syndrome Meiosis • Meiosis: A type of cell division where the chromosome number is reduced to half. The process in which cells undergo two dividing phases to form gametes. Meiosis only produces sex cells (gametes). Meiosis Gametes are your sex cells. Your egg and sperm cells. Sexual reproduction (sperm + egg)produces a zygote. Meiosis Diploid vs. Haploid • Diploid Number (2n): the number of chromosomes found in all body cells. Humans 46. -found in the somatic(body) cells • Haploid Number (n): 1/2 the diploid number of chromosomes. Humans 23. – found in the egg and sperm cells of a species DIPLOID HAPLOID Diploid vs. Haploid Organism Diploid # (body cells) Haploid # (sex cells) Human 46 23 48 Chimpanzee 24 39 Dog 78 8 Fruit fly 4 7 Garden pea 14 630 Adder’s fern 1260 Terms • Gametes: eggs or sperm • Gonads: specialized organs in higher animals where the gametes are made • Ovaries: female gonads • Testes: male gonads Meiosis Meiosis I • Has all the phases mitosis has. I P M A T Meiosis II • Has all the phases meiosis I has, except Interphase. P M A T Prophase I of Meiosis • During Prophase 1 crossing over takes place. • Crossing over is : the exchange of chromosome pieces. – Crossing over increases the variability of the offspring – This is why the offspring of sexual reproduction show many variations - Crossing over occurs only during Prophase I Mitosis vs. Meiosis Problems during Meiosis Normally, homologous chromosomes separate and move toward opposite poles of the cell. – Problems during anaphase: this disorder is called non Disjunction – Nondisjunction: the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate Nondisjunction • Down's syndrome: results from the nondisjunction of chromosome 21 – individual has an extra 21st chromosome Down’s Syndrome Rates Mistakes in Mitosis can be Good • polyploidy: having an entire extra set of chromosomes – Will result in the 3n or 4n number of chromosomes - Many plants are a result of polyploidy; banana & day lily Summary of Mitosis & Meiosis 1. Meiosis is very similar to two divisions of mitosis. 2. The diploid number (2n) of chromosomes is reduced by half to the haploid number (n) 3. Eggs and sperm are formed 4. Crossing Over causes lots of variations 5. Variations rarely occur in MITOSIS 6. Variations often occur in MEIOSIS Summary 7. Mitosis is associated with asexual reproduction. 8. Mitosis takes place in somatic (body) cells. 9. What is produced from mitosis? Two identical daughter cells How many? 4 10. Meiosis is associated with sexual reproduction. 11. Meiosis takes place in sex cells. 12. Meiosis produces gametes and three polar bodies.