* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Punnett_Squares
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
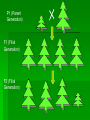
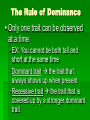
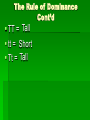
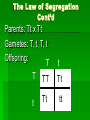
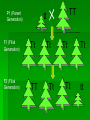
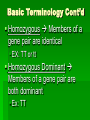
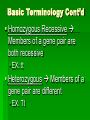
Rules of Genetics Gregor Mendel Carried out important studies in heredity Heredity passing on characteristics from parent to offspring Characteristics that are inherited are called traits Mendel’s Experiment Mendel chose to work with pea plants because they reproduce sexually Which means they produce male and female sex cells, or gametes The male gamete, pollen, unites with the female gamete, egg, and results in a fertilized cell (zygote) Mendel’s Experiment Cont’d Mendel dusted the pollen from one plant onto the egg of another plant By doing this Mendel was sure exactly which parents produced the offspring he was researching Mendel’s Experiment Cont’d He carefully controlled his experiments by researching only one trait at a time The tall pea plants had been tall for many generations and had always produced tall offspring The short pea plants had been short for many generations and had always produced short offspring Mendel’s Experiment Cont’d Mendel then crossed these parent plants to produce new plants Hybrid the offspring of parents that have different forms of a trait P1 (Parent Generation) F1 (Filial Generation) F2 (Filial Generation) Mendel’s Experiment Cont’d Think of your family: Your parents are the P1 Generation You are the F1 Generation Any children you might have are the F2 Generation Mendel’s Results The Rule of Unit Factors The Rule of Unit Factors Mendel concluded that each organism has two factors that control each of its traits Gene Section of a chromosome that determines a specific trait of an organism The Rule of Unit Factors Cont’d Genes exist in different forms Allele Alternate gene form EX: Gene = height Allele = tall or short Offspring inherit one allele from each parent The Rule of Dominance Only one trait can be observed at a time EX: You cannot be both tall and short at the same time Dominant trait the trait that always shows up when present Recessive trait the trait that is covered up by a stronger dominant trait The Rule Of Dominance Cont’d Dominant traits are represented by uppercase letters EX: T Recessive traits are represented by lowercase letters EX: t The Rule of Dominance Cont’d TT = Tall tt = Short Tt = Tall The Law of Segregation Every individual has two alleles of each gene When gametes are formed each receives one of these alleles During fertilization these gametes randomly pair to produce four combinations of alleles The Law of Segregation Cont’d Parents: Tt x Tt Gametes: T, t, T, t Offspring: T T TT t Tt t Tt tt P1 (Parent Generation) TT tt F1 (Filial Generation) Tt F2 (Filial Generation) TT Tt Tt Tt Tt Tt tt The Law of Independent Assortment Genes of different traits are inherited independently of one another EX: Plant height and seed color EX: Blond hair and blue eyes Basic Terminology Genotype the genetic makeup of an organism EX: TT, tt Phenotype the physical appearance of an organism EX: Tall, Short Basic Terminology Cont’d Homozygous Members of a gene pair are identical EX: TT or tt Homozygous Dominant Members of a gene pair are both dominant Ex: TT Basic Terminology Cont’d Homozygous Recessive Members of a gene pair are both recessive EX: tt Heterozygous Members of a gene pair are different EX: Tt