* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Whole Genome Polymorphism Analysis of Regulatory Elements in
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
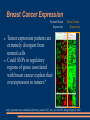
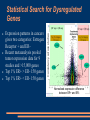
Whole Genome Polymorphism Analysis of Regulatory Elements in Breast Cancer Jacob Biesinger Dr. Garry Larson City of Hope AAGTCGGTGATGATTGGGACTGCTCT[C/T]AACACAAGCGAGATGAAGAAACTGA Topics Covered Today Molecular Cause of Genetic Disease Cancer and Gene Regulation Combining Data: Bioinformatics Progress So Far http://medicine.osu.edu/lend/Portfolios/0506/AR Port/files/SICKLE CELL WEBSITE/whatissickle.htm Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Genetic Disease SNPs in coding regions: Phe Pro Glu Val Thr STOP Ser ATGCCGGCTTACCATA A T TCTACCTAAATCCGGT Genetic disease may also be caused by differential expression of vital proteins Promoter Binding Mechanism Sickle Cell Anemia TGTAGA ATGCCGGCTTACCATA T ATCTACCTAAATCCGGT Micro RNA Binding Mechanism Protein Coding Region Chunky sheep from miRNA binding site destruction Untranslated region Nature Rev. Genet. 5, 202–212 (2004) Breast Cancer Expression Normal Breast Expression Breast Tumor Expression Tumor expression patterns are extremely divergent from normal cells Could SNPs in regulatory regions of genes associated with breast cancer explain their overexpression in tumors? http://genome-www.stanford.edu/breast_cancer/cell_line_review2001/images/figure2.html Expression patterns in cancers gives two categories: Estrogen Receptor + and ERRecent metaanalysis pooled tumor expression data for 9 studies and >15,000 genes Top 1% ER+ > ER- 150 genes Top 1% ER+ < ER- 150 genes Consistency across studies Statistical Search for Dysregulated Genes Normalized expression difference between ER+ and ER- Regulation Motifs Which TF binding sites exist in our selected genes? A recent study identified motifs conserved in regulatory regions across 4 organisms lymphocyte transmembrane adaptor 1 Promoter motifs: 123 known motifs 174 phylogenetically conserved Downstream motifs: 273 conserved 3’ UTR 343 conserved miRNA 6mer 368 conserved miRNA 7mer Motif Search Use Python and UCSC Genome Browser to: Get promoter region DNA (2kb upstream from transcription start site (TSS) + max of 2kb downstream of TSS, limited by translation start) Get 3’ untranslated region RNA Search for motifs on + and – strand Results for Top 1% up and down: 22206 known motif hits 23475 phylo motif hits 9559 3’ UTR hits 42846 6mer hits 11719 7mer hits SNP Databases HapMap ~4 million CGEMS ~550k SNP information is coming from two databases: HapMap- Four groups (270 total people) genotyped for same SNPs CGEMS- Breast Cancer association study, complete with p-values. A late-comer to our study (June 2007) Mapping SNPs Gene Promoters and 3’ UTR HapMap ~4 million CGEMS ~550k Motif Matches Use MSSQL 2003 and Python (pymssql) to perform a join of dbSNP, HapMap and CGEMS SNPs with regulatory motifs Verify Motif Significance How do we know that these motifs are significant? Hypothesis: Due to negative selection, there will be fewer SNPs in motifs than in random areas within the same region. Method: Contrast how many motifs have at least one SNP in them against how many of 100 random sequences from the same region have at least one SNP in them Motif Counting Results Known Top 1% Actual Random 1-Sided PMotif with Snp Motif without Snp Total Value 97 18394 18491 0.000009494 14630 1834470 1849100 Total 14727 1852864 1867591 1-Sided PValue Phylo Top 1% Actual 130 19363 19493 Random 16499 1913438 1929937 Total 16629 1932801 1979430 0.001889 3’ UTR results not yet available There is a significant difference between motifs and random sequences. CGEMS Results A number of SNPs that fall within motifs are associated with Breast Cancer Highest ranking was 1514 out of 550,000 Further analysis required to say if significant Thanks! SoCalBSI mentors City of Hope Dr. Garry Larson Dr. David Smith Dr. Päl Sætrom Cathryn Lundberg All the SoCalBSI students! Funded by: