* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heredity - Madison County Schools
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
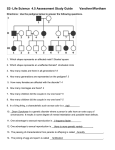
Heredity Mrs. Foles 2010-2011 Jag Mark 9/27/10 • Supply a definition for a mutation. Include information on what can cause a mutation, as well as, effects from a mutation. Jag Mark 9/28/10 • In humans, brown eyes (B) are dominant over blue (b). A brown-eyed man marries a blue-eyed woman and they have three children, two of whom are brown-eyed and one of whom is blue-eyed. Draw the Punnett square that illustrates this marriage. What is the man’s genotype? What are the genotypes of the children? Jag Mark 9/29/10 • In pea plants, yellow peas are dominant over green peas. Use a Punnett square to predict the phenotypic and genotypic outcome (offspring) of a cross between a plant heterozygous/hybrid for yellow (Yy) peas and a plant homozygous/purebred for green (yy) peas. Jag Mark 9/30/10 • Mendel performed a genetic experiment by crossing two pea plants that are heterozygous for their purple flower color. The results of his cross yielded 125 white pea plants and 375 purple pea plants. • What is the ratio of white to purple pea plants? • What is the ratio of purple pea plants to total pea plants? • Which color is the recessive trait? Jag Mark 10/1/10 • What biological process produces sex cells? • How do sex cells differ from body cells? • Explain why it is necessary to make sex cells through a process separate from mitosis. Jag Mark 10/4/10 1. Physical appearance of traits 2. Inherited combination of alleles 3. Process that produces sex cells 4. Process through which bacteria reproduce 5. Mathematical chance an event will occur A. B. C. D. E. Probability Genotype Binary Fission Phenotype Meiosis Jag Mark 10/5/10 • Supply a definition for a genetic disorder. • What can cause a genetic disorder? • Are genetic disorders typically the result of dominant or recessive genes? • Give an example of a genetic disorder. Jag Mark 10/6/10 • Here is a pedigree for an inherited lung disease. Provide the genotypes of each of the individuals marked with lower case letters. Determine if they are male or female. Jag Mark 10/7/10 • Compare and contrast hybrid and purebred organisms. Jag Mark 10/8/10 1. Two forms of the same gene 2. Each allele has its own degree of influence 3. Structure of DNA 4. Process produces sex cells 5. Mutation in these cells can be passed down to offspring A. B. C. D. E. F. Meiosis Double Helix Alleles Sex Cells Body Cells Incomplete Dominance Jag Mark 10/11/10 1. Keeps the cytoplasm inside 2. Largest and most visible organelle 3. Smallest and most abundant organelle 4. Releases energy 5. Gives plants green color A. Chlorophyll B. Ribosome C. Nucleus D. Mitochondria E. Cell Membrane Jag Mark 10/12/10 • One of Mendel’s experiments resulted in 705 plants with purple flowers and 224 plants with white flowers. – What is the ratio of the purple-flowered plants to all the offspring obtained from this experiment? – What is the ratio of the purple flowers to white flowers? Jag 10/13/10 • Compare and contrast selective breeding and genetic engineering. Jag 10/14/10 • Test Day! • Clear Desk except for sheet of notebook paper and a pencil. Who do you look like? • Heredity is the passing of traits from parent to offspring. • First person to notice the trend of heredity was Gregor Mendel who studied pea plants. Why Studying Peas? • Grow quickly and self pollinate • Mendel studied only 1 trait at a time, but 7 total traits – Example: height, seed shape, flower color • Trait: is a distinct phenotypic characteristic of an organism that may be inherited. – Example: Eye color Fun with Peas! • Mendel made sure to study true-breeding plants (which means that they produce the same offspring type each time) – Example: Tall always makes tall. • Mendel cross-pollinated the true-breeding plants to see what would happen. How Did the New Pea Plants Look? • The parent generation of one tall plant and one short plant breed together made 100% new tall plants in the F1 generation. • He concluded that tall is a dominant trait over short the recessive trait. – Dominant: represented by a capital letter (T). Masks the recessive allele – Recessive: represented by a lower case letter (t). Is masked by the dominant allele. 2nd Experiment • Mendel cross pollinated two plant in the F1 generation and found that about 75% were tall and 25% were short. What did this mean? • Mendel determined that instructions for these results must be found on genes. • Each parent contributes a gene, two forms of a gene make an allele. • To test this theory, Mendel invented a Punnett square. Genotype/Phenotype • Genotype: The genetic makeup or allelic makeup. – Ex. (TT, Tt, tt) • Phenotype is the appearance of a trait. – Ex. (tall, short) • Two dominant alleles is homozygous dominant. (TT) • One dominant allele and one recessive allele is heterozygous. (Tt) • Two recessive alleles is homozygous recessive. (tt) Making a Punnett Square • First, make a table with 4 squares inside. • Next, place the alleles from the parents on the top and the left hand side of the big square. • How would Punnett Squares look from the P generation and the F1 generation? Practice • Make a Punnett square to predict whether or not a child will have dimples using a parent that is homozygous recessive and one that is heterozygous. (Dimples are dominant.) Incomplete Dominance • When one trait is not completely dominant over another. The result is a combined phenotype. – Ex. Snap dragons: Red Crossed with White Codominance • Occurs when both alleles for a gene are expressed equally. – Ex. Blood Type Probability • Probability is the mathematical likelihood that something is the case or will happen • May expressed as a fraction or as a percent. – Ex. Flipping a coin • ½ chance of coin landing on heads and ½ chance of coin landing on tails • 50% chance of coin landing on heads and 50% chance of coin landing on tails Why we are all so different? • Because of sexual reproduction!! Which is when a man’s sperm cell joins with a woman’s egg cell. These cells are called sex cells or gametes. • Sex cells only contain half of a normal body cell’s chromosomes. • Therefore sex cells must be made by a process other than mitosis. • When two sex cells combine they form a zygote. Meiosis • Sex cells are made from meiosis!!!!! • Meiosis is basically mitosis twice without replication after the initial mitosis. The result is four cells with half the genetic information as the original cell. These new cells are called haploid cells. • Each body cell has 46 chromosomes. Each sex cell has 23 chromosomes. • Homologous Chromosomes: pairs of chromosomes Meiosis Are you a boy or a girl? • Sex Chromosomes determine your sex. • Males have one X sex chromosome and one Y sex chromosome. (XY) • Females have two X sex chromosomes. (XX) Karyotype • Map of chromosomes • Is this a male or female? • How can you tell? Probability • What is the probability of – Having a girl? – Having two girls in a row? – Having three girls in a row? • What is the probability of having a boy after having three girls in a row? • First Draw a Punnett Square!!! Genetics in Action • Selective Breeding: involves crossing of organisms with desired traits to maximize their potential • Ex. Flowers, fruits, vegetables, animals (cows) – Benefits of genetic engineering: recombinant DNA used to make bacteria produce insulin. Genetic Engineering • Faster form of selective breeding, where genetic information is changed in an organism. • Removing one piece of DNA and inserting a more desired piece of DNA. Genes in Action • Purebred: Organism results from crossing two organisms with similar traits – Advantages: • Predictable – Disadvantages: • Undesirable traits get passed on • Lack of genetic variation (problems if disease occurs) – Example: • TT x TT = TT • Labrodor dogs • Hybrid: Organism produced from crossing two organisms with different traits. – Advantages: • Variety • Maximize desirable traits – Disadvantages: • Unpredictable – Example: • TT x tt = Tt • Tomato plants Genetics in Action • Pedigree: a tool used to trace a particular trait throughout a families generations • □ squares=males • Ο circles=females • Vertical lines connect children to their parents • Solid squares or circles indicate the presence of the trait • Half-filled squares or circles indicates that the person is a carrier for a particular trait. Pedigree Reproduction • Asexual reproduction: – Requires only 1 parent – Does not involve sex cell production – Occurs in bacteria, archea, as well as some fungi and plants • Binary fission: bacteria • Budding: sponge • Sexual reproduction – Requires two parents – Involves fertilization of two gametes (sex cells) produced from meiosis When Genetics Goes Wrong • Genetic disorders: are disorders caused by abnormalities in the DNA as the result of mutations or errors during meiosis. – Most are congenital (born with) – Most are due to recessive genes; therefore both parents must be a carrier to affect the child. • Genetic disorders: Cystic Fibrosis, Trisomy 21 (Down’s Syndrome), Sickle Cell Anemia Trisomy 21 • Individuals with Down’s Syndrome have an extra chromosome 21 due to problems in meiosis. • Symptoms: retarded, smaller head and body, slanted eyes due to folds in skin. • Risks increase after mother is 35. Trisomy 21 Cystic Fibrosis • Occurs in 1 in 2,500 (common among Caucasian) • CF is a "multi-system" disease, meaning that it affects many body organs. (Mostly the lungs and the digestive system.) • Normally, mucus is watery. It keeps the linings of certain organs moist and prevents them from drying out or getting infected. In CF, an abnormal gene on chromosome 7 causes mucus to become thick and sticky. • The mucus builds up in your lungs and blocks the airways. This makes it easy for bacteria to grow and leads to repeated serious lung infections. These infections can cause serious damage to the lungs. Cystic Fibrosis • The thick, sticky mucus can also block in the pancreas. As a result, digestive enzymes that are produced by the pancreas cannot reach your small intestine or help break down food. The intestines do not absorb fats and proteins fully. • As a result: – Nutrients leave your body unused, and lead to malnutrition. – Stools become bulky. – Lack vitamins A, D, E, and K. – May lead to intestinal gas, a swollen belly, and pain or discomfort. Cystic Fibrosis • Both parents must be a carrier for the child to have cystic fibrosis. • The average survival is now more than 30 years and have a greater than 80% chance of living into their late forties Sickle-Cell Anemia • Normal RBCs – Are donut shaped with the centers partially scooped out and are soft and flexible – Pass easily through blood vessels – Live about 120 days • Sickle RBCs – Are Stiff, sticky, and distorted in shape – have difficulty passing through small blood vessels leading to possible death of tissue – Live about 16 days Sickle-Cell Anemia Genetic counselors • Genetic counselors can aid people who want to have children, but are afraid of passing a disease on to their children.