* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gregor Mendel and Genetics
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
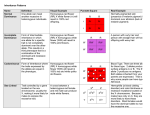
Bellringer 11/5/13 What is the relationship between DNA and the way you look? Topic: Introduction into genetics EQ: What is genetics? Genetic Material The nucleus of a cell contains genetic material DNA chromosomes genes -> Alleles www.kent.edu/projects/cell/page7.htm Who was Gregor Mendel and what is genetics? Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk in the mid-nineteenth century. He carried out the first important studies of heredity by using pea plants. Genetics is the branch of biology that studies heredity. Inheritance Occurs when traits are passed down from parent to child. Traits The different versions of a characteristic Example: blue, green, and brown eyes What is heredity? Heredity is the passing on of characteristics from parents to offspring. The characteristics that are passed down are called traits. Gregor Mendel’s Monohybrid Cross (p.156 in science book) A monohybrid cross is when you cross two plants that differ only by one trait. 1st Generation= 2nd Generation= 3rd Generation= Tall Peas X short Peas All tall Peas ¾ produced tall peas (75%), ¼ produced short peas (25%) The Rule of Unit Factors After seeing what happened Mendel concluded that there are two factors that control each trait. We now know that these factors are called genes. Each gene has different forms that are called alleles. One allele is inherited from each of the parents. Genes and Alleles Each chromosome has information about thousands of traits Gene- section on chromosome that has information for one trait See page 174 Genes Genes are short sections of chromosomes http://www.accessexcellence.org What are Genes? Factors that are passed from one generation to the next… Genes come in different forms called alleles: ex: tall and short Some are seen and some are not Genes come in pairs Since chromosomes come in pairs (one from mom, one from dad) Genes come in pairs http://anthro.palomar.edu/biobasis/images/ karyotype_male.gif The Rule of Dominance When the offspring inherit two different alleles for one trait, the trait that is expressed is said to be dominant while the other is recessive. In Mendel’s pea plants that had one allele for tall and one allele for short, the peas were tall because tall is the dominant trait. Recessive Dominant Genes Dominant: those traits that are seen Recessive: those traits that are not seen Thus came the principle of dominance: some are dominant and others are recessive Recessive allele Recessive allele Martin Sheen Charlie Sheen Talk about dominant genes!!! Kirk Kirk Douglas Michael Emilio Estevez Activity Cut out figure 3 pg. 166 Answer the Visual Check #7. Be sure to use the terms dominant and recessive in your answer. Genotypes and Phenotypes A Genotype is a specific combination of alleles. A Phenotype is the visual trait that is expressed. Tall Allele Possible Generation= TT Possible Genotypes= TT short Allele Tt Tt Tt Tt Possible Phenotypes= Tall, Tall, Tall, short tt tt Homozygous and Heterozygous An organism is homozygous dominant for a trait if both of the alleles carry the dominant gene. RR = Homozygous dominant (pure) An organism is said to be homozygous recessive for a trait if the alleles both carry the recessive gene. rr = Homozygous recessive (pure) An organism is heterozygous for a trait if the two alleles are different. Rr = Heterozygous (Hybrid) 1st Generation= Tt X T t 2nd Generation= Tt T TT t Tt Tt tt TT, Tt, Tt, tt Genotype Ratio = 25% homozygous tall, 50% heterozygous tall, 25% homozygous short Phenotype Ratio = 3 Tall, 1 short Using Alleles in Mendel’s Experiment Tall Allele P1 Generation= Short Allele TT X tt Punnett Square – a tool used to visualize all the possible combinations of alleles from the parents Genotype Ratio = 100% Tt (heterozygous Tall) Phenotype Ratio = 100% Tall 0% short t Tt t Tt T T Tt Tt Pea Plant Traits