* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tumor-suppressor genes - School District of New Berlin
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
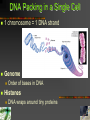
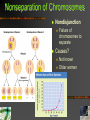
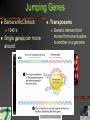
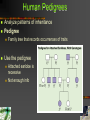
Human Genetics Biology: Exploring Life Campbell, Williamson, Heyden Prentice Hall 1 12.1 The nucleus contains an information richgenome. 2 DNA Packing in a Single Cell 1 chromosome = 1 DNA strand Genome Order of bases in DNA Histones DNA wraps around tiny proteins 3 Human Genome Project Determine the sequence and functions of all human chromosomes “rough-draft” done in 2000 Introns vs exons Coding vs non-coding 4 12.2 Accidents affecting chromosomes can cause disorders. 5 Down Syndrome Abnormal chromosomes Trisomy 21 Miscarriage Down Syndrome Three chromosomes 21 Characteristics Facial features Below-average height Heart defects Immune dysfunction Mental disability 6 Nonseparation of Chromosomes Nondisjunction Failure of chromosomes to separate Causes? Not known Older women 7 Damaged Chromosomes Duplication Deletion Fragment is lost Inversion Part of chromosome is duplicated Reversing a fragment Translocation Fragment attaches to non-homologous 8 Jumping Genes Barbara McClintock 1940’s Single genes can move around Transposons Genetic element that moves from one location to another in a genome 9 12.3 Mendel’s principles apply to humans. 10 Human Pedigrees Analyze patterns of inheritance Pedigree Family tree that records occurrences of traits Use the pedigree Attached earlobe is recessive Not enough info 11 Disorders Inherited as Recessive Traits Carrier Has copy of allele but does not show symptoms Range of severity Albinism Tay-Sachs Major nerve damage Cystic Fibrosis 1/25 from European decent Defective protein secretes excessive mucus 12 Disorders Inherited as Dominant Traits Examples Extra fingers and toes Achondroplasia Heterozygous Two copies – fatal 99.99% population has homozygous recessive Recessive alleles sometimes common Death Huntington's Disease Middle-age nervous system degeneration Chromosome #4 13 Sex-linked Disorders Most located on X chromosome ♂ only needs one “bad” allele ♀ needs both “bad” alleles 14 Predicting and Treating Genetic Disorders Genetic counselor Tests before birth Collects, analyzes and explains patterns of inheritance Trisomy 21 Tests after birth Phenylketonuria (PKU) Causes metal disability 15 12.4 Genetic Changes contribute to cancer. 16 Cancer Genes Pics Growth factor Initiate cell division Tumor-suppressor genes Breast cancer Brain cancer Immune system attacks cancer Proteins to stop cell division Oncogene Cancer causing gene 17 “Inherited” Cancer Always is from damaged or changed DNA Not passed from parent to child if non-sex cell Mutated tumorsuppressor-gene BRCA1 More likely to form breast cancer 18 Permission Statement Restricted to the use of New Berlin Eisenhower High School (New Berlin, WI) Students, Faculty and Staff. Contact the Science Department for usage permissions. ©2006 19