* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Genetics Notes Continued Honors Bio
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
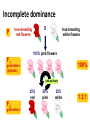
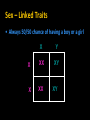
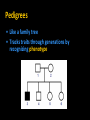
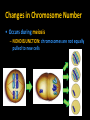
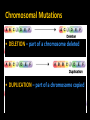
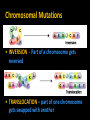
Non – Mendelian Genetics *Not all traits follow Mendel’s rules! *Not all traits follow the rules! • Some don’t have dominance! • Some have more than one dominant trait! • Some are regulated by many genes, not just one! • Some are dependent on your gender! – Sorry guys :( Incomplete dominance • Heterozygote shows a blended phenotype – Example: • RR = red flowers • WW = white flowers • RW = pink flowers – make 50% less color RR RW WW Incomplete dominance P X true-breeding red flowers true-breeding white flowers 100% pink flowers F1 100% generation (hybrids) self-pollinate 25% red F2 generation 50% pink 25% white 1:2:1 Co-dominance • 2 alleles affect the phenotype equally & separately – not blended phenotype – Example: ABO blood groups • 3 alleles – IA, IB, i – IA & IB alleles are co-dominant » Both expressed – i allele recessive to both What is the phenotype? A •I i • I Bi • IAIA A B A A B •I I AB B B •I I B • ii O Sex-linked Traits • First 22 pairs of chromosomes are called AUTOSOMAL CHROMOSOMES • Last pair is the SEX CHROMOSOMES – Females: XX – Males: XY Sex – Linked Traits • Always 50/50 chance of having a boy or a girl X Y X XX XY X XX XY Human X chromosome Duchenne muscular dystrophy Becker muscular dystrophy • Sex-linked – usually means “X-linked” – more than 60 diseases on genes on X chromosome Chronic granulomatous disease Retinitis pigmentosa-3 Norrie disease Retinitis pigmentosa-2 Ichthyosis, X-linked Placental steroid sulfatase deficiency Kallmann syndrome Chondrodysplasia punctata, X-linked recessive Hypophosphatemia Aicardi syndrome Hypomagnesemia, X-linked Ocular albinism Retinoschisis Adrenal hypoplasia Glycerol kinase deficiency Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency Incontinentia pigmenti Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome Menkes syndrome Androgen insensitivity Sideroblastic anemia Aarskog-Scott syndrome PGK deficiency hemolytic anemia Anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia Agammaglobulinemia Kennedy disease Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy Choroideremia Cleft palate, X-linked Spastic paraplegia, X-linked, uncomplicated Deafness with stapes fixation PRPS-related gout Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease Alport syndrome Fabry disease Lowe syndrome Immunodeficiency, X-linked, with hyper IgM Lymphoproliferative syndrome Hunter syndrome Hemophilia B Hemophilia A G6PD deficiency: favism Drug-sensitive anemia Chronic hemolytic anemia Manic-depressive illness, X-linked Colorblindness, (several forms) Dyskeratosis congenita TKCR syndrome Adrenoleukodystrophy Adrenomyeloneuropathy Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy Diabetes insipidus, renal Myotubular myopathy, X-linked Albinism-deafness syndrome Fragile-X syndrome Lesch-Nyhan syndrome HPRT-related gout Human X-chromosome • Women have 2 copies – Getting one “bad” X has little/no effect • other X will compensate • Men have only 1 copy – Getting one bad X chromosome gives them the disease • No backup X • Ex. Colorblindness – Hemophilia – Balding Hemophilia sex-linked recessive HY HH XHHh Xh x X XH female / eggs male / sperm XH XH Y XH XH XH Y XH Xh Xh XH Xh XH Xh XhY carrier disease XHY Y Pedigrees • Like a family tree • Tracks traits through generations by recognizing phenotype Pedigrees • represent females • represents males • Shading represents “affected individual” • Half shading (if present) represents carrier Polygenic Inheritance • Traits with more than one gene controlling their expression Environmental Effects on Traits • Some genes are activated by the environment – Ex: Fur color in animals Chromosomal Abnormalities • Problems can arise when chromosomes are changed – – – – Too many Too few Parts missing Parts added Changes in Chromosome Number • Occurs during meiosis – NONDISJUNCTION: chromosomes are not equally pulled to new cells Chromosomal Mutations • DELETION – part of a chromosome deleted • DUPLICATION – part of a chromosome copied Chromosomal Mutations • INVERSION - Part of a chromosome gets reversed • TRANSLOCATION – part of one chromosome gets swapped with another Karyotypes • Used to ID chromosomal abnormalities Normal Karyotype • • • • 2 copies of each autosomal chromosome 2 X’s in females; 1 X, 1 Y in males No deletions or insertions No extra copies