* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics - Georgia Highlands College
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
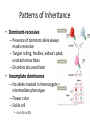
Genetics Chapter 29 Essential Must Know Terminology • Chromosome: structure of DNA seen in cell division – Homologous chromosomes • Autosomes: 22 homologs w/o effecting sex • Sex chromosomes: 1 homolog determines sex – Karyotype: display of homologs • Gene: trait determining sequence of DNA – Alleles: different or alternate versions • Dominant: masks presence of other alleles (A) • Recessive: easily masked by other alleles (a) – Genotype: allelic combination • Homozygous dominant: two dominant alleles (AA) • Heterozygous: one dominant and one recessive allele (Aa) • Homozygous recessive: two recessive alleles (aa) – Phenotype: allelic combination physically seen/shown Sources of Genetic Variation • Segregation – Random alignment in metaphase for separation in anaphase • Independent assortment – Homologs segregate independently of other homologs • Crossing over – Synapse of tetrad and exchange at chiasma (when? review) • Random fertilization – No control over which sperm or egg Solving Genetic Problems • Punnett Squares helpful to ‘predict’ probability – Each event independent – Larger # of offspring = better prediction – Key points: • All individuals have 2 alleles for EVERY gene – 1 from mom and 1 from dad • Meiosis produces haploid gametes from diploid cells – Aa mother = A or a eggs • Practicing – Place gametes (haploid) of one parent along top, other along the left side – Combine all possible female gametes with all possible male gametes = fertilization – Boxes with 2 alleles = possible offspring (diploids) Patterns of Inheritance • Dominant-recessive – Presence of dominant allele always masks recessive – Tongue rolling, freckles, widow’s peak, unattached earlobes – Disorders discussed later • Incomplete dominance – No alleles masked in heterozygote = intermediate phenotype – Flower color – Sickle cell • ss vs Ss vs SS Patterns of Inheritance (cont.) • Multiple alleles/ Codominance – Traits w/ 2+ alleles – Varying relationships – Blood type • Sex-linked – Genes on sex chromosomes – X-linked when on X only (most) • Males only need 1 = hemizyogus • Females need 2; 1 = carrier – Colorblindness and hemophilia (discussed later) Patterns of Inheritance (cont.) • Polygenic – 2+ genes in multiple locations working together – Broad spectrum of phenotypes – Skin color (3 genes), height, intelligence • AABBCC = darkest, aabbcc = lightest, others = in between • Environmental relationships – Maternal drug use/environment during embryonic development – Nutrition and diet – Hormonal alterations Abnormal Chromosome Number Disorders • Normally due to nondisjunction • Turner syndrome: female w/ 45 chromosomes (X0) – Underdeveloped reproductive organs = sterile, short, broad neck, lack 2° sex characteristics • Klinefelter syndrome: male w/ 47 chromosomes (XXY) – Underdeveloped reproductive organs = sterile, lack facial hair, some breast enlargement, long appendages • Down syndrome: 47 chromosomes (trisomy 21) – Slanted eyes, flattened face, short stature, gradient of mental retardartion Autosomal Disorders • Dominant – Rare because always expressed embryo/fetal death – Huntington’s disease: impairs motor functioning • Onset after reproductive age, increase probability of passing • Recessive – More frequent, because of masking – Albinism: lack of pigmentation – Cystic fibrosis: thick mucus build up in lungs and GI tract Sex-linked Disorders • Need to represent sex chromosome and version – XN = trait not present, Xn = trait present • Red-green colorblindness • Hemophilia – Allele for clotting factor VIII mutated Genetic Screening • Pedigrees trace traits through generations – Family tree using phenotypic information • Fetal testing w/ known risk – Amniocentesis • Most common; after 14th week • Check for genetic markers, enzymes, or karyotypes – Chorionic villus sampling • 8th week possible, 10th recommended • Similar to above