* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mechanism of Evolution
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
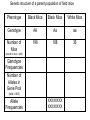
Population Genetics and Evolution AP Biology Population Genetics Macroevolution: evolution on a grade scale Ex. Evolution of a new species - modern camel Microevolution: change in the gene frequency within a population over time Ex. Peppered moths during the Industrial Revolution Genetics Language Review Alleles - alternate forms of a gene Ex. Height in plants - T = tall and t = short Alleles can be dominant or recessive Locus (pl. loci) - location of a gene on a chromosome Homozygous - two alleles are identical (tt) Heterozygous - two alleles are different (Tt) Genetics Language Review cont… Genotype - genetic make-up of an individual Phenotype - physical and physiological traits of an individual Incomplete Dominance - neither of the alleles are dominant and blending occurs red, white and pink flowers Co-dominant - both alleles for the trait are dominant black, white and black-white feathers in chickens Genetic structure of a parent population of field mice Phenotype Black Mice Black Mice White Mice Genotype AA Aa aa Number of Mice 196 168 36 (total # of mice = 400) Genotype Frequencies Number of Alleles in Gene Pool (total = 800) Allele Frequencies XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXX Phenotype Purple Purple White Genotype AA Aa aa Number of Flowers 320 160 20 (total # of flowers = 500) Genotype Frequencies Number of Alleles in Gene Pool (total = 1000) Allele Frequencies XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXX The Hardy-Weinberg Principle A way to determine how real populations change over time by developing a model of a population that does not change genetically from one generation to the next Actual populations can be compared to the hypothetical model If proportions of genotypes do not change from generation to generation, the genotypes are said to be in Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium The Hardy-Weinberg equation: 2 p + 2pq 2 +q =1 Where: p = frequency of dominant allele (ex. A) q = frequency of recessive allele (ex. a) p2 = frequency of individuals homozygous for allele A 2pq = frequency of individuals heterozygous for alleles A and a q2 = frequency of individuals homozygous for allele a Example: The dominant allele in a population has the frequency of 0.6 A) Find the frequency of the recessive allele NOTE: p + q = 1 (allele frequency) B) Find the frequencies of the genotypes in this population. NOTE: p2 + 2pq +q2 = 1 (genotypic frequency) Solution: Conditions for HardyWeinberg 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. The population is large (unaffected by random gene changes) Mating is random Isolation (no gene flow between populations) No mutations No natural selection (no genotype has a reproductive advantage over another)