* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
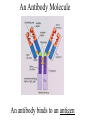
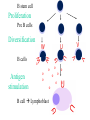
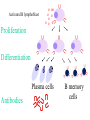
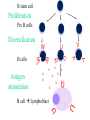
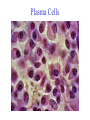
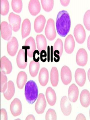
The Magic of Lymphocytes Cells that take the form of lymphocytes T cells cytotoxic helper cells suppressor cells B cells NK (natural killer) cells Stem cells Possible others pro-mast cells ?? pro-dendritic cells ?? Maturation of B and T Cells small lymphocyte lymphoblast (prolymphocyte) Small Lymphocytes can Switch back and forth into Lymphoblasts T. SL = small lymphocyte Blast = lymphoblast An Antibody Molecule An antibody binds to an antigen Antibody Genes are Cut and Spliced mRNA transcript Remove introns The exact position of gene splicing is variable. End of a v segment Beginning of a d segment |G.G.A|C.A.T. ……… T.C.G|T.C.C|G.G.G variable splicing |G.G.A|C.A.G ----------- |T.C.C|G.G.G |G.G.A|C.A. ----------- G|T.C.C|G.G.G |G.G.A|C. ----------- C.G|T.C.C|G.G.G |G.G.A|C.A.G------- T.C.G|T.C.C|G.G.G |G.G.A|------------------ T.C.C|G.G.G Lymphocytes insert extra nucleotides into their DNA at junction sites in a non-templated manner. |G.G.A|C.A.T. …………… T.C.G|T.C.C|G.G.G |G.G.A|C.A.T|N.N.N|N.N.N|T.C.G|T.C.C|G.G.G The Clonal Selection Theory Proposes a two stage process for antibody formation. B stem cell Proliferation Pre B cells Diversification B cells Antigen stimulation o o o o o o o o o o B cell Lymphoblast o o o Activated B lymphoblast o oo o o o o o o Proliferation Differentiation Plasma cells Antibodies B memory cells B stem cell Proliferation Pre B cells Diversification B cells Antigen stimulation o o o o o o o o o o B cell Lymphoblast o o o Plasma Cells T cells The T cell Receptor - is homologous to antibody. - forms by gene rearrangement. - varies from one T cell to another. but it - is always membrane-bound. - binds to peptides fragments of antigens These must be held on a cell surface by an MHC protein. Cells that take the form of lymphocytes T cells cytotoxic helper cells suppressor cells B cells NK (natural killer) cells Stem cells Possible others pro-mast cells ?? pro-dendritic cells ?? Activation of a T cell by an Antigen Presenting Cell Some Inerleukins Enuff