* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Hedgehog signaling pathway wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
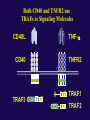
The Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Family
TNFRI
Fas
PV-A53R
Dr3
PV-T2
Dr4
Dr5
Dr6
TRID
DEATH
DOMAIN
OPG
TNFR II
CD40
CD30
CD27
LTR
4-1BB
OX40
NGFR
HVEM
GITR
RANK
Initial Approach:
The Yeast Two Hybrid System
CD40
Ring
Finger
N
Zinc Fingers
1
2
3
4
5 Zipper
TRAF-N
TRAF-C
C
TRAF3
Both CD40 and TNFR2 use
TRAFs as Signaling Molecules
CD40L
CD40
TRAF3
TNF-a
TNFR2
TRAF1
TRAF2
Structural Features of the TRAF
Family
Size
Expression
TRAF-N TRAF-C
Ring
TRAF1 409
Spleen, Lung, Testis
TRAF2 501
Ubiquitous
TRAF3 567
Ubiquitous
TRAF4 470
Multiple tissues
(non-lymphoid)
TRAF5 558
Spleen, Lung
TRAF6 522
Ubiquitous
Zinc fingers
Ile. zipper
TRAF Binding Specificity
TRAFs
Receptors
TNFR1
TNFR2
TRAF1
TRAF3
TRAF4
TRAF5
TRAF6
+, indirect +, indirect
+
CD27
CD30
TRAF2
+
CD40
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
4-1BB
+
+
+
Ox40
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
LTR
+
Fas
LMP-1
IL-1R
+
+
+
DcR1
Fas
Dr4
Dr5
DcR2
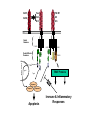
Death
Domains
{
{
FADD
TNF-R1
Dr3
Dr6
FADD
TRADD
Death Effector
Domains
TRAF2
RIP
mitochondria
Caspase-8
Type II
Type I
TRAF Proteins
Caspase 3
Caspase 7
Caspase 6
Apoptosis
Immune & Inflammatory
Responses
TLR -
Toll-like Receptor
• Family of receptors that bind to pathogenassociated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
• Evolutionarily conserved from Drosophila to humans
• Recognition of bacterial, fungal, and viral patterns
leads to rapid inflammatory response
TLR
LRR
TIR
Binds to conserved
chemical structure
Transduces signal to
downstream molecules
The Nod Superfamily:
Receptor for Intracellular Pathogens ?
TIR
NBS LRR
CARD NBS LRR
Pyrin NBS LRR
BIR
Innate Cells
NBS LRR
Nod2 mutations are responsible for 25% of human Crohn’s disease
TLR and Nod family proteins signal through TRAF6
TLR
MyD88
LRR
TIR TIR
DD DD
TRAF6
Ring
Finger
1
Zinc
Fingers
2 3 4
KD
IRAK
Nod
5
TRAF-N
TRAF-C
N
C
CARD NBS
KD
JNK
Extracellular
Pathogens
NF-kB
LRR
CARD
RIP2
Intracellular
Pathogens
T R A F
1 2 3 4 5 6
RELT
BAFF-R
4-1BB
CD27
TNF-R2
EDAR,AITR, Fn14, BCMA
CD40
XEDAR
TACI
LTR
Troy, OX40, HVEM, CD30
TNF-R1
Dr3
Dr6
TLR/IL-1R
ER lumen
Ring
Finger
TRAF
RANK
p75NGFR
RIP
TRADD
IRAK
MyD88
Death
Domains
LMP-1
IRE
1
1
Zinc
Fingers
2 3 4
N
N
TIM
Domains
CARD NBS LRR
5
TRAF-N
TRAF-C
C
A20
cIAPsECSITFilamin
GCKR MEKK1 NIK
MIP-T3 Peg3 T6BP
TANK TRIP TTRAP
P62 nucleoporin
TBK1 TNIK
PKC RIPs
KD
CARD
RIP2
ASK1
CDK9 C-Src GCK
TAK1
Nod
C
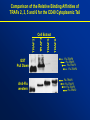
Comparison of the Relative Binding Affinities of
TRAFs 2, 3, 5 and 6 for the CD40 Cytoplasmic Tail
GST
Pull Down
Anti-Flu
western
TRAF6
TRAF5
TRAF3
TRAF2
Cell Extract
Flu-TRAF6
Flu-TRAF5
Flu-TRAF3
Flu-TRAF2
Flu-TRAF6
Flu-TRAF5
Flu-TRAF3
Flu-TRAF2
Defining the Residues within the CD40ct C17 Critical for
Binding Either TRAF2 or TRAF3
C238A
Q239A
P240A
V241A
T242A
Q243A
E244A
D245A
G246A
GST
L235A
H236A
G237A
TRAF3 Binding
TRAF2 Binding
GST
T234V
T234S
T234A
C17
GST
T234V
T234S
T234A
TRAF3
Binding
C17
CD40
GST
BEAD
C17
P230A
V231A
Q232A
E233A
T234A
TRAF2
Binding
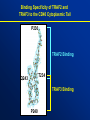
Binding Specificity of TRAF2 and
TRAF3 to the CD40 Cytoplasmic Tail
P230
TRAF2 Binding
T234
Q243
TRAF3 Binding
P240
DC
V241A
T234A
Q232A
P207A
CD40wt
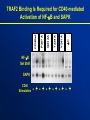
TRAF2 Binding Is Required for CD40-mediated
Activation of NF-kB and SAPK
NF-kB
Gel Shift
SAPK
CD40
Stimulation
- +- +- +- +- + - +
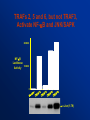
TRAFs 2, 5 and 6, but not TRAF3,
Activate NF-kB and JNK/SAPK
200000
NF-kB
Luciferase
Activity
100000
0
c-Jun (1-79)
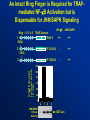
An Intact Ring Finger is Required for TRAFmediated NF-kB Activation but is
Dispensable for JNK/SAPK Signaling
Ring 1 2 3 4 5
1
NF-kB
JNK/SAPK
++
++
TF 5/C45A
-
++
TF 5/C81A
-
++
TRAF Domain
TRAF 5
C45A
2
C81A
3
NF-kB Dependent
Luciferase Activity
( X 1000)
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
C
JNK/SAPK
Kinase
Activity:
1
2
3
GST-Jun
TAK1
IRAKs TRADD
TRAF proteins as
adaptor molecules
NIK RIPs ASK1
GCKs A20 IAPs
TRIP TANK Pw1
TNFRs
Complex for SAPK activation
Ring
Finger
Zinc Fingers
1
2
3
4
5
TRAF-N
TRAF-C
N
C
Complex for NF-kB activation
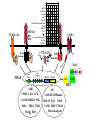
The TNF Receptor Superfamily
TNFRI
Fas
PV-A53R
PV-T2
Dr3
TRID
Dr4
Dr5
Dr6
OPG
DEATH
DOMAIN
TNFR II
CD40
CD30
CD27
LTR
4-1BB
OX40
NGFR
HVEM
GITR
RANK
TIM
The TLR Family
IL-1R
TLR1-?
RP105
TOLL1-?
18W
L6
RPP5
TIR
IRAKs/MYD88
TRAFs
FADD/TRADD/RIP
RIP2
FLICE (Caspase 8)
NIK
GCK/GCKR
Intermediate Caspases
IKK
MEKK
IkB
SEK
NF-kB
SAPK (JNK)
Terminal Caspases
APOPTOSIS
IMMUNE AND INFLAMMATORY RESPONSES
The Nod Family
High-Density Oligonucleotide Microarrays
CD40L- and LPS-Mediated B-Cell Activation
Bacterial/Fungal
Products
(e.g., LPS)
CD40 Ligand
TLR4
Interferon
Response
Genes
Innate Immune
Responses
CD40
Common genes
Survival
Proliferation
Ig Isotype Switching
Genes for Cell
Communication and
Germinal Center
T-dependent
Adaptive Responses
Combinatorial Regulation
Two factors required to activate each gene:
One factor required to activate each gene:
factor A
factor B
factor C
+1
A
A
B
B
C
C
A
B
A
C
B
C
Gene 1
+1
Gene2
+1
Gene 3
Gene 1
Gene 2
Gene 3
Gene 4
Gene 5
Gene 6
If the expression of each transcription factor
is unique, the expression pattern of each of
the 6 genes will be unique.
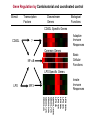
Gene Regulation by Combinatorial and coordinated control
Stimuli
Transcription
Factors
Downstream
Genes
Biological
Functions
CD40L Specific Genes
CD40L
Adaptive
Immune
Responses
?
Common Genes
Basic
Cellular
Functions
NF-kB
LPS Specific Genes
LPS
Innate
Immune
Responses
IRF3
LPS 168h
LPS 72h
LPS 24h
LPS 12h
LPS 4h
CD40L 168h
CD40L 72h
CD40L 24h
CD40L 12h
CD40L 4h
Enhanceosome at a Eukarytic Control Region
LPS-Specific Genes:
CD40L
Time
Interferon-Response?
LPS
Time
Gene
Description
IFIT3
Mx1
Interferon-Induced Protein w. Tetratricopeptide Repeats
Interferon-Induced GTPase
IFIT2
Interferon-Induced Protein w. Tetratricopeptide Repeats
IFIT1
Interferon-Induced Protein w. Tetratricopeptide Repeats
IRF7
Interferon Regulatory Factor 7
IFI204
Interferon-Activatable Protein 204
IFI35
Interferon-Induced 35Kd Protein
IFI203
Interferon-Activatable Protein 203
IRG1
Immune-Responsive Gene 1
IRF9
Interferon Regulatory Factor 9
IFI1
Interferon-Inducible Protein 1
D6-Pending D6 Chemokine Receptor
IFI-TM3l
Interferon-induced Transmembrane Protein 3-like
PKR
dsRNA-Activated Protein Kinase
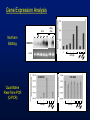
Gene Expression Analysis
LPS
Northern
Blotting
LPS+
CHX
RANTES
EthBr
LPS (h)
RANTES
18S RNA
Quantitative
Real-Time PCR
(Q-PCR)
LPS (h)
LPS (h)
TLR3/TLR4 Primary Response Genes*
5’ Regulatory
Regionf
GENE
Functional
Characteristics
IP-10/
CXCL10d
Chemotactic for numerous cell types
including Th1-subsets of T cells and NK
cells, inhibits angiogenesis, and exerts
direct antimicrobial activity by unknown
mechanism.
RANTES/
CCL5
Chemotactic for activated T cells,
macrophages, and DC’s. Neutralization of
RANTES shown to reduce Th1-type
granuloma formation.
IFN
d
.
Important cytokine secreted by virusinfected cells. Activates numerous antiviral and anti-growth defense mechanisms.
ISG15
Interferon-induced protein with structural
homology to ubiquitin. Shown to induce
proliferation of PBL’s and increase
cytolytic activity of NK cells.
IFIT1/
GARG16
Protein induced by inflammatory stimuli.
Has tetratricopeptide repeat domains
thought to be involved in protein
processing.
*Primary-Reponse defined as upregulated by LPS (100ng/mL) at 2h in the presence of cycloheximide (20mg/mL)
fSchematic representation of gene promoters created by using Celera web-based genomic database, TESS
promoter analysis software (http://www.cbil.upenn.edu/tess/) and the TRANSFAC transcription factor database.
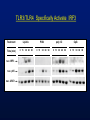
TLR3/TLR4 Specifically Activate IRF3
Treatment
Time (min)
nuc. IRF3
nuc. p65
nuc. USF2
Lipid A
0 15
30 60 90
PGN
0 15
30 60 90
poly I:C
0 15
30 60 90
CpG
0 15
30 60 90
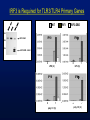
NF-kB is Required for TLR3/TLR4 Primary Genes
IkB-DA
Mock
Mock
LPS 30’
-
+
+
-
-
+
+
-
Tamoxifen
-
-
+
+
-
-
+
+
IP10
RANTES
IkB-DA
IFN
18S RNA
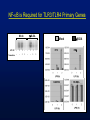
IRF3 is Required for TLR3/TLR4 Primary Genes
WT
IRF3
IRF3-DBD
61-
IRF3 53kD
49-
36-
IFN
IP10
IRF3-DBD ~34kD
0
1
1
LPS (h)
LPS (h)
IP10
0
0
IFN
1
poly I:C (h)
0
1
poly I:C (h)
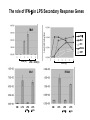
The role of IFN- in LPS Secondary Response Genes
Mx1
IFN
Mx1
IFI1
IFI204
IRF7
LPS (h)
LPS + CHX (h)
LPS (h)
Mx1
CM
LPS
LPS
aIFN
LPS
aIgG
IFI204
CM
LPS
LPS
aIFN
LPS
aIgG
LPS
IFN
MyD88
IRAK TRAF6
?
IKK NF-kB
Primary Response
• IP10
• RANTES
• IFN
• ISG15
• IFIT1
IkB
?
IRF3
IRF3 NF-kB
ISRE
STAT1a/
kB
ISRE / GAS
TYK2
JAK2
STAT1a/
Secondary Response
• Mx1
• IFI1
• IFI204
• IRF7