* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
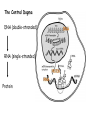
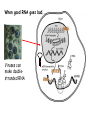
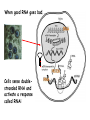
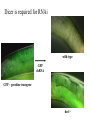
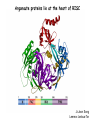
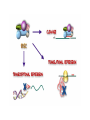
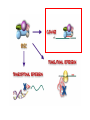
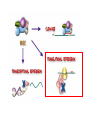
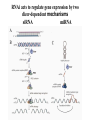
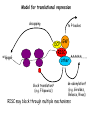
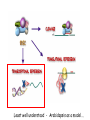
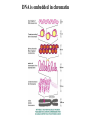
RNAi Mechanism The Central Dogma DNA (double-stranded) RNA (single-stranded) Protein When good RNA goes bad.... Viruses can make doublestranded RNA When good RNA goes bad.... Cells sense doublestranded RNA and activate a response called RNAi Understanding how RNAi works is the key to using it as a genetic tool and for therapy What is the mechanism of interference? RNAi in vitro... Cell free extract RNAi? Hannon Lab, Zamore Lab, Tuschl Lab, Sharp Lab Dicer cuts dsRNA into short RNAs Vanhecke, D.; Janitz, M. Drug Discov. Today, 2005, 10, 205-225. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference Emily Bernstein, Amy A. Caudy, Scott M. Hammond & Gregory J. Hannon 2001 Bernstein et al. Cloned Dicer, the RNase III enzyme that is evolutionarily conserved and contains helicase and PAZ domains, as well as two dsRNA-binding domains. Dicer is an evolutionarily conserved nuclease RNAi functions in many different organisms dsRNA Dicer is required for RNAi wild-type GFP dsRNA GFP – germline transgene dcr1-/- How do small dsRNAs turn genes off? Dicer-cut siRNA is used as a template to direct cleavage of complementary mRNA by RISC RISC: RNA-inducing silencing complex Argonaute proteins lie at the heart of RISC Ji-Joon Song Leemor Joshua-Tor PIWI is an RNase H like domain Argonaute-PIWI RNase HI RNase HII Ji Joon Song Leemor Joshua-Tor A model for siRNA directed cleavage microRNAs regulate gene expression without cleavage RNA or protein level small temporal RNAs (stRNAs) LIN-14, LIN-28 proteins LIN-41 protein lin-4 RNA let-7 RNA L1 stage L2 stage L3 stage LIN-29 protein L4 stage Adult stage • lin-4 miRNA represses translation of lin-14 (L1 to L2 moult) stRNA precursor Dicer stRNA Translational repression Banerjee & Slack, 2002 Ambros lab, Rukvun lab Mello lab, Zamore lab RNAi acts to regulate gene expression by two dicer-dependent mechanisms miRNA siRNA Model for translational repression M7GpppG RISC recognizes a target RISC AAAAAA......... Model for translational repression M7GpppG DCP GW RISC Other proteins are also recruited – either along with RISC or later other AAAAAA......... Model for translational repression decapping to P-bodies DCP GW RISC M7GpppG other block translation? (e.g. Filipowicz) AAAAAA......... de-adenylation? (e.g. Giraldez, Belasco, Rivas) RISC may block through multiple mechanisms Least well understood - Arabidopsis as a model…. DNA is embedded in chromatin Regulation of gene expression at the level of chromatin Sequence-independent linker histones: control DNA compaction and accessibility to trans-acting factors post-translational modifications of histone tails: control compaction of DNA and serve as docking sites for trans-acting factors Range: Can act at the level of a single gene, often acts over groups of genes and over larger domains (20-200kb), and can affect gene expression over an entire chromosome Model for siRNA-dependent initiation of heterochromatic silencing by RITS RITS: RNA-induced initiation of transcriptional gene silencing complex dsRNA-mediated silencing in various organisms: Multiple mechanisms that are Dicer-dependant Meister & Tuschl, 2004 dsRNA-mediated regulation may play a central role in the regulation of Gene Networks Levine and Davidson, PNAS, 2005 Ke, et al. Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 2003