* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
DNA paternity testing wikipedia , lookup
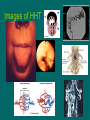
Utilization and Impact of a New Diagnostic Genetic Test for Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) SUMR Scholar: Brittany Milliner Mentor: Shimrit Keddem Principal Investigator: Barbara Bernhardt Center for the Integration of Genetic Healthcare Technologies (Penn CIGHT) Genetics 101 Nucleotides DNA Genes Chromosomes • The study of inherited traits and variation in living organisms. • DNA is composed of a chain of four different types of nucleotides—the sequence of these nucleotides is the genetic information organisms inherit. • Genes correspond to regions within DNA that code for certain traits • Genes are arranged linearly along long chains of DNA sequence, called chromosomes. Genetics 102 • Children receive one copy of their chromosome from their mother and one from their father • Humans have 46 chromosomes (23 copies) • Alleles are variations of a gene • Some of the traits that we have are based on simple inheritance where one version of a gene (dominant allele) masks the expression of the other version of that gene (recessive allele) • Mutations are any change in an organisms’ DNA Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) • • • • Autosomal dominant disorder Mutation in one of at least 5 genes Affects approx. one in 5000 individuals Diagnosed by (Curacao Criteria): 1. 2. 3. 4. Epistaxis (nosebleeds), Telangiectases, Brain and visceral arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). Family history • Nearly all people with HHT have a positive family diagnosis • A definitive diagnosis of HHT requires positive findings in 3 of 4 of the criteria; “suspect” if two • Signs and symptoms are age-dependent and there is great variability in severity, even in one family Images of HHT Genetic Testing • Testing became available in November 2003 • Shows vulnerabilities to inherit diseases • If a mutation can be identified in a person with definite HHT, relatives can be screened for that particular diseasecausing mutation to determine definitively whether or not they are affected • Genetic testing was unusually marketed to patients (consumers) rather than providers • Costly imaging studies and surveillance would then be recommended only for those family members who carry mutations What is the problem that needs to be addressed? • Many individuals with HHT remain undiagnosed or even if diagnosed, may not be managed appropriately • Left untreated, AVMs can lead to stroke, brain abscess, transfusion dependency and death Goals of the Study 1. 2. 3. 4. To describe the development and pattern of early utilization of a new genetic test To compare the economic impact of two methods for diagnosing HHT in families To collect further data on reasons for testing, understanding of test results, reactions to testing, and barriers to testing To use online deliberation to explore stakeholders’ views about screening and to develop policy recommendations Online Deliberations • Individuals with HHT or an affected first degree relative, health care providers and genetic testing lab personnel were recruited • Reminder phone calls • 75 minutes of pre-arranged “chat information” designed to assess views of testing, who should get it, barriers, who should order it, and implications of results • 12 discussions included people with HHT or their first degree relatives – Approx. 10 individuals per patient group • There were also 2 groups of mixed providers (physicians, genetic counselors, lab personnel), with approx. 8-10 participants per group • Pre- and post-surveys were completed Patient Demographics • • • • • • 92.4% have been diagnosed with HHT 41.2% have had genetic testing 73.1% of participants were female 92.4% were Caucasian 92.4% had at least some college Average age: 52.3 years The Good, The Bad, & The Ugly • • • • • • • • • Wide range of patient group dynamics “I bleed mostly inside my nose and sinuses and mouth, and I have a lung AVM” “We are such a ‘bloody’ funny group” “Trashcans full of our own blood” “Last transfusion I had, I walked in dressed as Dracula, the nurses loved it…” “Do your dogs like your used tissues, or is it just mine?” “I believe it is also our responsibility as patients to educate our doctors. We have a rare disease and what's wrong with taking the bull by the horns, so to speak?” “A stigma you can live with. A fatality from HHT you can't.” “The first step to treating HHT is diagnosis” More Quotes • “An important issue is to try to calculate the numbers and cost to public health so that HHT becomes an important disease to cure. In the future, genetic testing will be done in the womb with transplants of the chromosomes that were missing.” • “If your children are negative, there is no need for your to get genetic testing.” • “If no other family history before Colleen, good chance she is not yet diagnosed. If no family memories of past generations having had symptoms, she might still consider genetic testing. This thing can skip lots of folks in the family.” Analyzing Data • Transcripts were formatted and uploaded to NVivo • Data was coded twice: for general and specific categories • Summaries were written for selected nodes NVivo Preliminary Data • • 119 Participants Summaries for: – – – – – – Barriers to Genetic Testing Importance of Genetic Testing Implications of Test Results for Child and Proband PCP Ordering Test Other Physicians Ordering Test Family Response to Being Approached More Data • Barriers: – Denial – Cost – Lack of Knowledge/Misinformation • Ordering testing: – PCP’s responsibility to order testing; part of care – Specialists and HHT Centers are also capable • Family response: – Some get tested, others don’t – “That darn denial again” Next steps • Continue data analysis • Develop recommendations to improve diagnosis and screening • Disseminate recommendations Project #2: Chart Abstraction •Scanned paper medical records for the following information: – – – – – – Genetic Mutation – Ethnicity – Procedures done Marital Status Curacao Criteria Met – Complaint of Headaches or Migraines – Pulse ox Height and Weight Signs of Generalized Connective Tissue Disorder Aortic root diameter Acknowledgements …