* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 9
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
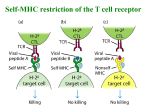
Chapter 9 T-cell Receptor Dr. Capers Kindt • Goldsby • Osborne Kuby IMMUNOLOGY Sixth Edition Chapter 9 T-Cell Receptor Copyright © 2007 by W. H. Freeman and Company T cell receptor vs B cell receptor T cell receptor is only membrane bound ○ Doesn’t appear in soluble form like antibodies so more difficult to assess it’s structure Antigen binding of T cell receptor is weaker than that of antibodies Antigen recognized by T cells is not antigen alone but antigen associated with MHC molecules (a) T cell receptor (TCR) is specific for peptide A (b) Right MHC haplotype but wrong antigen (peptide B) (c) Right antigen (peptide A) but wrong haplotype T cell receptor (TCRs) ○ TCR heterodimers are similar to immunoglobulins Therefore they are classified in immunoglobulin superfamily Resembles Fab fragment TCRs ○ Associate with MHC – αβ TCR ○ Do not associate with MHC – γδ TCR - Much remains to be learned of function of γδ TCR Rearrangement of TCR genes Similar to that of Ig Rearrangement of α and γ chains ○ V, J, and C segments Rearrangement of β and δ chains ○ V, D, J, and C segments Generation of TCR diversity (a lot like Ig) ○ Multiple germ-line gene segments ○ Combinatorial V-(D)-J joining ○ Junctional flexibility ○ P-region nucleotide addition ○ N-region nucleotide addition ○ Combinatorial association of light and heavy chains However, there is no somatic mutation with TCR ○ May be to ensure that after thymic selection, the TCR doesn’t change to cause self-reactive T cell TCR-CD3 Complex Accessory molecules help in signal transduction after interaction of T cell with antigen 2 Zeta ζζ chains Heterodimer of delta epsilon γε chains Heterodimer of delta epsilon εδ chains T cell accessory molecules T cells can be divided into 2 populations: ○ CD4+ Recognize antigen associated with Class II MHC OR ○ CD8+ Recognize antigen associated with Class I MHC ○ CD4 and CD8 function as coreceptors and assist with signal transduction Affinity of TCR for peptide-MHC complexes is enhanced by coreceptors Allogenic – genetically different individuals of same species Alloreactivity of T cells is puzzling: ○ Evidence supports that T cells can only respond to antigen+MHC ○ However, T cells can recognize a foreign MHC molecule alone - As with transplants