* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Complex Patterns of Inheritance
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
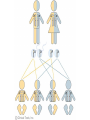
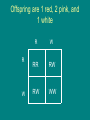
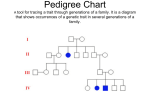
Complex Patterns of Inheritance Mendel’s Laws Law of Segregation: • Organisms inherit two copies of each gene, one from each parent • Organisms donate only one copy of each gene in their gametes. Thus, the two copies of each gene segregate, or separate, during gamete formation. Law of Independent Assortment: the alleles of different genes separate independently of one another during gamete formation I. Sex-linked traits • A sex-linked trait is a trait whose allele is located on either the X or Y chromosome. A) Hairy Ears: Gene on the Y Chromosome B) Most sex-linked traits on X chromosome are recessive • Examples include: hemophilia, red-green colorblindness, and a form of muscular dystrophy A person with red-green color blindness sees a number 2 Hemophilia • In this pedigree, only males are affected, and sons do not share the phenotypes of their fathers. – Thus, hemophilia is linked to a sex chromosome–the X. • Expression of hemophilia often skips generations. – Thus, it is recessive. Extensive bruising of the left forearm and hand in a patient with hemophilia. Genotypes for females XHXH = normal blood clotting, non-carrier XHXh = normal blood clotting, carrier of gene XhXh = female with hemophilia Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom was a carrier of hemophilia Genotypes for Males • XHY = normal blood clotting • XhY = male with hemophilia • Tsarevich Alexei of Russia had hemophilia Cross a carrier mother with a normal father. No daughters with hemophilia, ½ of sons with hemophilia XH Xh XH XHXH XHXh Y XHY XhY Cross a hemophiliac father with a normal (non-carrier) mother. All daughers are carriers, no sons have hemophilia. XH XH Xh XHXh XHXh Y XHY XHY II. Incomplete Dominance • An individual displays a trait that is intermediate between the two parents • Example: a red snapdragon crossed with a white snapdragon produces pink offspring Red = RR, White = WW, Pink = RW Make a Punnett square for a red plant crossed with a white plant All offspring are pink, with RW genotype W W R R RW RW RW RW What happens if you cross two pink snapdragons? Offspring are 1 red, 2 pink, and 1 white R W R W RR RW RW WW 1 red (RR), 2 pink (RW), 1 white (WW) Incomplete dominance in horse coat color III. Codominance • Two dominant alleles are expressed at the same time • Roan coat color in horses or cows is an example • A roan horse has both red and white hairs • Roan has red and white hairs Parents Codominance in chicken feather color. Black and White feathers IV. Multiple Alleles • Genes with three or more alleles for a particular trait. • Examples are the ABO blood types, fur color in many animals. Coat color in rabbits Phenotype Allele ch Pattern of Inheritance Dominant to all other alleles Dominant to Himalayan and white Dominant to white c recessive Dark gray coat C Chinchilla (silver-gray) cch Himalayan (white with dark ears) White 1. List all possible genotypes for a: a) dark gray-coated rabbit CC, Ccch, Cch, Cc b) chinchilla rabbit cchcch, cchch, cchc c) Himalayan rabbit c hc h, c hc d) white rabbit cc 2. Predict the phenotype for a rabbit with a chcch genotype chinchilla Predict the phenotype for a rabbit with a Cch genotype dark gray 3. Would it be possible to obtain white rabbits if one parent is white and the other is chinchilla? Yes, if the chinchilla parent has a white allele 4. Would it be possible to obtain chinchilla rabbits if one parent is Himalayan and the other is white? No, because chinchilla is dominant to both Himalayan and white, so the allele couldn’t be “hiding”. 5. A chinchilla rabbit is mated with a Himalayan. Some offspring are white. What are the parents’ genotypes? Himalayan is chc and chinchilla parent is cchc V. Polygenic traits • Traits that are influenced by 2 or more genes • Examples include human height, weight, hair color, eye color, and skin color Coat color in Labrador retrievers Coat color in Labrador retrievers VI. Epistasis • One gene that interferes with the expression of other genes. • Example is with albinism. • One gene interferes with all other genes for pigment production. VII. Traits influenced by the environment. • Color of hydrangea flowers (blue in acidic soil, pink in basic soil) • Color of arctic fox • Human height, skin color, behavior