* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Alternative Pathways to Cellular Respiration!
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sink wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
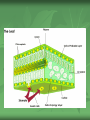
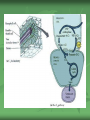
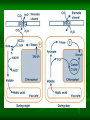
Alternative Pathways to Cellular Respiration! By: Julia Sigman, Izzie Gall, Kalah Haley, Valencia Watson C4 Pathway C4 stands for 4 carbon In order for the Calvin Cycle to take place, Rubisco must carry carbon dioxide to a 5 carbon molecule (Ribulose bisphosphate) during carbon fixation OH NO! When carbon dioxide levels are low, rubisco has a hard time finding the carbon dioxide and needs assistance Without the carbon dioxide, the calvin cycle cannot occur In such cases, CO2 goes through stoma and goes to the mesophyll cell So what do we do about it? Once in the mesophyll cell, we find PEP carboxylase, a 3C molecule The CO2 then comes in and forms a 4C molecule (oxaloacetate) The molecule rearranges to make the CO2 able to be broken off easier. From there, the CO2 breaks off and a 3C molecule (pyruvate) is left to go through the cycle again What the what? Basically, without rubisco carrying the CO2 the calvin cycle cannot fuction thus photosynthesis cannot occur. When CO2 levels are low and rubisco has trouble finding it the CO2 travels through the stomata into the mesophyll cell and PEP carboxylase finds it and gives the CO2 to rubisco Once the rubsico has the CO2 it travels to the bundlesheath cell, where it surrounds the vein, thus the calvin cycle can continue What could go wrong? The problem with the C4 pathway is that it uses ATP in addition to the ATP used in the calvin cycle When pyruvate is left after the CO2 breaks off the malate, it takes ATP to rearrange the pyruvate into PEP. Who would do this? Organisms that perform the calvin cycle are corn and sugar cane. CAM Pathway CAM stands for Crassulacean Acid Metabolism The CAM pathway is specific for day and night The CAM pathway is utilized by plants that close their stomata during the day in order to prevent evaporation of their water Sleepover!! Plants close their stomata during the day As in C4 plants, the CAM Pathway uses PEP Carboxylase to fix a carbon molecule to a 4 Carbon molecule forming oxaloacetate The oxaloacetate is rearranged and converted into malate, which is stored in cell vacuoles overnight (aka there is a CO2 slumber party) Ba-BAM! Because the plants close their stomata during the day the CO2 gets backed up in the plant The CO2 is stored overnight in the malate During the day, when the stoma are closed, CO2 is removed from the stored malate and enters the Calvin Cycle and photosynthesis can continue What are examples of CAM plants? Pineapples and cacti The problem with the CAM cycle is, like the C4 pathway, it uses additional ATP.