* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download hinge regions are already ready to serve as a catalytic center
Bimolecular fluorescence complementation wikipedia , lookup
Structural alignment wikipedia , lookup
Protein folding wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Protein domain wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Alpha helix wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
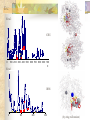
Dynamic Hinge Regions co-localize with Biological Important Residues lecturer : Lee-Wei Yang May 21 2002 Assumption : biological catalytic residues colocalized in the dynamic hinge regions of proteins. remove homologues seq.; no bias to specific protein family Method : PDB Search Protein & inhibitor complex (randomly) Literature Search Residues in Active(or catalytic) site Dynamic Analysis by GNM Dynamic patterns in active or inhibitory sites (Slow1,2) Results Table 1 25 proteins, their relative inhibitors and biologically critical residues Only 25 proteins out of 140 were suitable for the following study by reasons of: 1.No or insufficient inhibition or catalyst sites information in the related literature 2. Inhibitor itself is huge polypeptide with carbon number larger than 40 3.Sequences have incomplete chain information Fig1 Active and inhibitor binding residues located on the hinge region of representative modes of protein motion.Except proteins in 1A42,1A5I, 1AL8, 1BH6, 1BVV, 1CRU are analyzed by global second slowest mode (slow mode 2), the rest of them were analyzed in global slowest mode (slow mode 1). Fig2 Structure diagram of proteins and inhibitors generated by Sting Millennium Table2 Percentage score and their average for each residues in active and inhibitory sites Ex. 1ARZ Ex: Slow2 1CRU 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 100 0 Slow1 1BH6 0 100 200 300 (by sting millennium) Table 2. Percentage score and average for residues in active and inhibitory sites PDB code Active site Amino acid Slow1(%) Slow2(%) B-exp(%) Slow1avg Slow2 avg B-exp* avg. 4.92 6.05 average of 25 proteins 13.91 Slow1avg Slow2 avg B-exp* avg. AVG 5.99 PDB code inhibition site Amino acid 8.41 average of 110 points Slow1(%) Slow2(%) 15.92 B-exp(%) AVG 9.86 7.34 average of 161 points # Inhibitory sites 17.74 10.32 8.63 15.68 average of 25 proteins Discussion # Metal ions #One interesting point is that, even we did not provide inhibitor information in the GNM calculation, the hinge regions are already ready to serve as a catalytic center before the possible substrate or inhibitor binding. Conclusion This study provides a general idea of the beneficial effect that biological macromolecules set their catalytic centers in the dynamic hinge region. Future Work 1. Collect more proteins 2. Generalize the reasons for proteins which have their active sites in the peak regions