* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macromolecules - Dickinson ISD
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biological aspects of fluorine wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
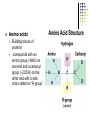
Macromolecules Carbon Compounds Carbon is an extremely versatile element. It has 4 valence electrons allowing it to bond with almost any other element. It can bond to other Carbon atoms, allowing it to form chains. These carbon-carbon bonds can be single, double or triple covalent bonds. Chains can close up on themselves and form rings. Every living organism has carbon in it Organic Macromolecules Large molecules made from thousands of smaller molecules. Formed by polymerization: the building of large compounds by joining smaller ones together. Monomers- the smaller compounds. Polymers- the larger compounds. Four groups of macromolecules (organic compounds) carbohydrates lipids nucleic acids proteins 3. Carbohydrates Compounds made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms. These atoms are usually in a ratio of 1:2:1. Living things use carbohydrates as a main source of energy. Examples – Plants Animals Two types of Carbohydrates Monosaccharidessingle sugar molecules. Examples: glucose and galactose found in milk Fructose found in fruits Polysaccharides- large sugars formed from monosaccharides. Examples: Starches Glycogen sugar storage molecule in animals Cellulose structural support in plants 4. Lipids Made mostly from carbon and hydrogen atoms. Not soluble in water. (does not dissolve in water) Consist of fats, steroids, oils and waxes Used to store energy. Some are important parts of biological membranes and waterproof coverings. Two types of lipids Saturated fats- all carbons have the maximum number of hydrogens attached to them. Usually are solid at room temperature Ex: beef, lard, butter, milk products Unsaturated fatscontain at least one carbon-carbon double covalent bond. Usually are liquid at room temperature Ex: cooking oils, nuts 5. Nucleic Acids Made up of hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon and phosphorus. Formed from monomers called nucleotides. Nucleotides- When joined together makeup the structural units of DNA & RNA. Store and transmit hereditary or genetic information. RNA-ribonucleic acid contains the sugar ribose. DNA-deoxyribonucleic acid contains the sugar deoxyribose Proteins Made up of nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Formed from monomers called amino acids. Examples of protein in nature: Spider Silk Collagen (in tennis racket) Hair Feathers Amino acids Building blocks of proteins compounds with an amino group (-NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (-COOH) on the other end with a side chain called an “R-group” Each protein has a specific role regulates cell processes Enzymes – speed up the rate of reactions forming muscles and bones transporting substances into or out of cells fighting disease