* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nucleic Acids
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
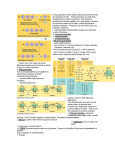
The Macromolecules of Cells: Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acid 2-1 Organic Molecules * Organic molecules are found in living things (vs. Nonorganic) * Referred to as “macromolecules” -- Carbohydrates -- Lipids -- Proteins -- Nucleic Acids 2-2 Organic molecules are made of carbon and can form a huge variety of carbon backbone chains. 2-3 Macromolecules (polymers) are formed from smaller building blocks called monomers. Polymer carbohydrates proteins nucleic acids Lipids Monomer monosaccharides amino acids nucleotides “none” 2-4 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates (sugars) serve as 1) quick energy and short-term energy storage 2) they play a structural role in plants, bacteria, and insects 3) many end in the suffix “ose” 2-5 Monosaccharides • Monosaccharides are sugars that are made up of only one sugar. • There are only 3 monosaccharides Glucose Fructose Galactose 2-6 Monosaccharide -one sugar carbohydrate Glucose 2-7 Disaccharides • Disaccharides are made out of two simple sugars (monosaccharides) Sucrose (table sugar) -- glucose + fructose Maltose (malt sugar) -- glucose + glucose Lactose (milk sugar) -- galactose + glucose 2-8 A disaccharide is made from linking two monosaccharides together. 2-9 Reactions • The making or breaking of disaccharides uses a molecule of water • Condensation: reaction makes a disaccharide from two monosaccharides and removes a water molecule in the process. • Hydrolysis: reaction breaks down a disaccharide by adding a water molecule to satisfy the exposed bonding sites on the two new monosaccharides. 2-10 Condensation Reaction • Water is removed to allow the two sugars to bond together. 2-11 Hydrolysis Reaction • Water is added so Oand OH+ can be added to exposed bonding sites. • Satisfies bonds 2-12 Polysaccharides Larger sugars are made from linking many glucose molecules Starch Glycogen Cellulose Chitin 2-13 Examples of Polysaccharides: starch -- (helical structure) energy storage in plants glycogen (highly branched) quick energy for animals cellulose -- (unbranched) found in plants for structure. It is not available as an energy source because of structure. Chitin – found in the exoskeleton of insects and crustaceans 2-14 Starch • Starch is a storage molecule for plants. It is stored in structures called plastids. • Starch is high in energy and is stored energy for the plant. 2-15 Glycogen • Glycogen is a molecule that is used by animals for temporary storage of energy. If not utilized, energy will be stored as fat. 2-16 Chitin • Chitin is a polysaccharide found in exoskeletons of crustaceans and insects. 2-17 Cellulose • Polysaccharide found in the cell walls of plants. Strong molecule used for structure and support of the plant cell. 2-18 Lipids *Lipids serve as long-term energy stores in cells, form membranes, and serve as hormones and insulation. Lipids do not dissolve in water!!! Main reason why lipids are classified together; all other molecules are soluble in water 2-19 Structure of Triglycerides Formed from a glycerol molecule and three fatty acid molecules. 2-20 Fatty Acid Chains Fatty acids are long chains of carbons with many hydrogens attached. Full of energy since all bonds are potential energy for an organism. Fatty acids may be saturated fatty acids or unsaturated fatty acids. 2-21 Saturated vs. Unsaturated “bad for you” • Saturated Fats have no double bonds • Found in tropical oils and animal fats • All carbons are “saturated” with hydrogens. • Straight chains • Solid at room temp. “good for you” • Unsaturated Fats have varying numbers of double bonds • Common in plants • All carbons are not fully bonded with hydrogens • Chains are bent at double bonds • Liquid at room temp. 2-22 Some lipids are phospholipids that form cell membranes. These only have two fatty acids chains. Glycerol head is hydrophilic -- loves water Fatty Acid tails are hydrophobic -- hate water 2-23 Other lipids are steroids -no fatty acid chains. Examples: Steroids -- Cholesterol (thickens arteries and is important in cell membrane) Hormones (estrogen and testosterone) Waxes 2-24 Proteins Proteins: 1. Serve as structural proteins (cartilage, fingernails, hair, etc.) 2. Act as enzymes to speed reactions 3. Serve as transport carriers 4. Act as antibodies 5. Allow materials to cross membranes 2-25 Proteins are polymers of amino acids. 2-26 Water is removed when joining two amino acids. 2-27 Proteins have levels of organization. 2-28 Protein Organization • Primary Structure (1°) -- linear chain of amino acids. Number and sequence of amino acids varies. • Secondary Structure(2°) -- shortening of amino acid chain by coiling or pleating • Tertiary Structure (3°) -- further folding of chain to create a more compact structure • Quaternary Structure (4°) -- only some proteins have this structure which is two or more chains bonded together. 2-29 Nucleic Acids Nucleotides are monomers of nucleic acids. Examples include Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic Acid (RNA). 2-30 2-31 DNA is double-stranded, with complementary base pairing. 2-32