* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Objective 11 Notes Tuesday Jan 17
History of molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Personalized medicine wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
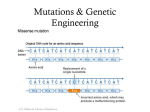
OBJECTIVE 11 NOTES Explain the evolutionary significance of a nearly universal genetic code The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology • What is it? – This is the term used when DNA is transcribed into RNA and RNA is translated into a protein. • Why does this work? – Because of the common genetic code What is the genetic code? Think Pair Share Talk to your classmates: What is the result of the common coding for amino acids? How is this important in genetic engineering /biotechnology? What do we mean by a nearly universal genetic code? DNA Evidence for Evolution Similarities • Living organisms share a common mechanism that copies and translates heritable genetic information. • All living organisms translate the genetic code using ribosomes. • They all translate it with the aid of small molecules called transfer RNA. • They all read it in the same direction, and they all read it in the same way, translating the code 3 letters at a time into sequences of amino acids, the building blocks of proteins. DNA Evidence for Evolution Differences • In some organisms, a handful of these 3-letter “words” have different meanings. Our own cells, for example, contain mitochondrial DNA in which 4 of the 64 words have different meanings from the “standard” code. In most organisms, these differences are so slight as to be trivial. • In common molds, for example, the sequence “UGA” is translated into the amino acid tryptophan. In the standard code, it's a “stop” signal. The other 63 words, however, are identical between humans, elephants, daisies, and molds. Mitochondrial DNA differences in Red from the Universal Code What else? • 48 of the 64 words are identical in all living organisms, and only 16 are known to vary across the enormous diversity of living things. • In fact, the entire biotechnology industry is built upon the universality of the genetic code. How Does DNA Relate to Evolution? • Mutations (changes) in DNA provide a source of genetic variation. • Commonalities in DNA between all organisms on Earth provide evidence for common descent. • Slight differences in the genetic code reflect branching evolutionary relationships.